A Case Report published in BMCNutr discusses selenium deficiency and scurvy due to an imbalanced diet of snacks and lacto-fermenting drinks in a 7-year-old boy with autism spectrum disorder.
] in ASD children, there are no reports of ASD children having a combination of scurvy and selenium deficiency. In this report, we describe a case of an ASD child with scurvy and selenium deficiency due to an imbalanced fixed diet of snacks and lacto-fermenting drinks.A 7-year-old boy was referred to our hospital due to gingival bleeding for 4 months. He was born a twin at term by caesarean section with a birth weight of 2.51 kg. There were no prenatal or postnatal complications.
Laboratory studies showed AST, 98 IU/L: 24–38 µg/dL); ALT, 64 IU/L; CK, 45 IU/L ; TSH, 2.55 µIU/mL ; FT4, 1.36 ng/dL ; vitamin C level, 1.1 µg/dL ; selenium level, 2.8 µg /dL ; retinol protein, 1.3 mg/dL ; vitamin B1, 22 ng/mL ; and folic acid, < 1.3 ng/mL . Echocardiograms did not show any pathological Q-wave or ST segment and T-wave changes. A lumbar and head MRI showed no hemorrhagic lesions.
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 scEvoNet: a gradient boosting-based method for prediction of cell state evolution - BMC BioinformaticsBackground Exploring the function or the developmental history of cells in various organisms provides insights into a given cell type's core molecular characteristics and putative evolutionary mechanisms. Numerous computational methods now exist for analyzing single-cell data and identifying cell states. These methods mostly rely on the expression of genes considered as markers for a given cell state. Yet, there is a lack of scRNA-seq computational tools to study the evolution of cell states, particularly how cell states change their molecular profiles. This can include novel gene activation or the novel deployment of programs already existing in other cell types, known as co-option. Results Here we present scEvoNet, a Python tool for predicting cell type evolution in cross-species or cancer-related scRNA-seq datasets. ScEvoNet builds the confusion matrix of cell states and a bipartite network connecting genes and cell states. It allows a user to obtain a set of genes shared by the characteristic signature of two cell states even between distantly-related datasets. These genes can be used as indicators of either evolutionary divergence or co-option occurring during organism or tumor evolution. Our results on cancer and developmental datasets indicate that scEvoNet is a helpful tool for the initial screening of such genes as well as for measuring cell state similarities. Conclusion The scEvoNet package is implemented in Python and is freely available from https://github.com/monsoro/scEvoNet . Utilizing this framework and exploring the continuum of transcriptome states between developmental stages and species will help explain cell state dynamics.
scEvoNet: a gradient boosting-based method for prediction of cell state evolution - BMC BioinformaticsBackground Exploring the function or the developmental history of cells in various organisms provides insights into a given cell type's core molecular characteristics and putative evolutionary mechanisms. Numerous computational methods now exist for analyzing single-cell data and identifying cell states. These methods mostly rely on the expression of genes considered as markers for a given cell state. Yet, there is a lack of scRNA-seq computational tools to study the evolution of cell states, particularly how cell states change their molecular profiles. This can include novel gene activation or the novel deployment of programs already existing in other cell types, known as co-option. Results Here we present scEvoNet, a Python tool for predicting cell type evolution in cross-species or cancer-related scRNA-seq datasets. ScEvoNet builds the confusion matrix of cell states and a bipartite network connecting genes and cell states. It allows a user to obtain a set of genes shared by the characteristic signature of two cell states even between distantly-related datasets. These genes can be used as indicators of either evolutionary divergence or co-option occurring during organism or tumor evolution. Our results on cancer and developmental datasets indicate that scEvoNet is a helpful tool for the initial screening of such genes as well as for measuring cell state similarities. Conclusion The scEvoNet package is implemented in Python and is freely available from https://github.com/monsoro/scEvoNet . Utilizing this framework and exploring the continuum of transcriptome states between developmental stages and species will help explain cell state dynamics.
Read more »
 Circulating amino acid levels and colorectal cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition and UK Biobank cohorts - BMC MedicineBackground Amino acid metabolism is dysregulated in colorectal cancer patients; however, it is not clear whether pre-diagnostic levels of amino acids are associated with subsequent risk of colorectal cancer. We investigated circulating levels of amino acids in relation to colorectal cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) and UK Biobank cohorts. Methods Concentrations of 13-21 amino acids were determined in baseline fasting plasma or serum samples in 654 incident colorectal cancer cases and 654 matched controls in EPIC. Amino acids associated with colorectal cancer risk following adjustment for the false discovery rate (FDR) were then tested for associations in the UK Biobank, for which measurements of 9 amino acids were available in 111,323 participants, of which 1221 were incident colorectal cancer cases. Results Histidine levels were inversely associated with colorectal cancer risk in EPIC (odds ratio [OR] 0.80 per standard deviation [SD], 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.69–0.92, FDR P-value=0.03) and in UK Biobank (HR 0.93 per SD, 95% CI 0.87–0.99, P-value=0.03). Glutamine levels were borderline inversely associated with colorectal cancer risk in EPIC (OR 0.85 per SD, 95% CI 0.75–0.97, FDR P-value=0.08) and similarly in UK Biobank (HR 0.95, 95% CI 0.89–1.01, P=0.09) In both cohorts, associations changed only minimally when cases diagnosed within 2 or 5 years of follow-up were excluded. Conclusions Higher circulating levels of histidine were associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer in two large prospective cohorts. Further research to ascertain the role of histidine metabolism and potentially that of glutamine in colorectal cancer development is warranted.
Circulating amino acid levels and colorectal cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition and UK Biobank cohorts - BMC MedicineBackground Amino acid metabolism is dysregulated in colorectal cancer patients; however, it is not clear whether pre-diagnostic levels of amino acids are associated with subsequent risk of colorectal cancer. We investigated circulating levels of amino acids in relation to colorectal cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) and UK Biobank cohorts. Methods Concentrations of 13-21 amino acids were determined in baseline fasting plasma or serum samples in 654 incident colorectal cancer cases and 654 matched controls in EPIC. Amino acids associated with colorectal cancer risk following adjustment for the false discovery rate (FDR) were then tested for associations in the UK Biobank, for which measurements of 9 amino acids were available in 111,323 participants, of which 1221 were incident colorectal cancer cases. Results Histidine levels were inversely associated with colorectal cancer risk in EPIC (odds ratio [OR] 0.80 per standard deviation [SD], 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.69–0.92, FDR P-value=0.03) and in UK Biobank (HR 0.93 per SD, 95% CI 0.87–0.99, P-value=0.03). Glutamine levels were borderline inversely associated with colorectal cancer risk in EPIC (OR 0.85 per SD, 95% CI 0.75–0.97, FDR P-value=0.08) and similarly in UK Biobank (HR 0.95, 95% CI 0.89–1.01, P=0.09) In both cohorts, associations changed only minimally when cases diagnosed within 2 or 5 years of follow-up were excluded. Conclusions Higher circulating levels of histidine were associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer in two large prospective cohorts. Further research to ascertain the role of histidine metabolism and potentially that of glutamine in colorectal cancer development is warranted.
Read more »
 Association of adverse respiratory events with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors among patients with type 2 diabetes in South Korea: a nationwide cohort study - BMC MedicineBackground Impaired respiratory function remains underrecognized in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D), despite common pulmonary impairment. Meanwhile, there is little data available on the respiratory effects of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i). Hence, we examined the association between SGLT2i use and the risk of adverse respiratory events in a real-world setting. Methods We conducted a population-based, nationwide cohort study using an active-comparator new-user design and nationwide claims data of South Korea from January 2015 to December 2020. Among individuals aged 18 years or older, propensity score matching was done to match each new user of SGLT2is with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4is), with patients followed up according to an as-treated definition. The primary outcome was respiratory events, a composite endpoint of acute pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), pneumonia, and respiratory failure. Secondary outcomes were the individual components of the primary outcome and in-hospital death. Cox models were used to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs. Results Of 205,534 patient pairs in the propensity score matched cohort, the mean age of the entire cohort was 53.8 years and 59% were men, with a median follow-up of 0.66 years; all baseline covariates achieved balance between the two groups. Incidence rates for overall respiratory events were 4.54 and 7.54 per 1000 person-years among SGLT2i and DPP4i users, respectively, corresponding to a rate difference of 3 less events per 1000 person-years (95% CI − 3.44 to − 2.55). HRs (95% CIs) were 0.60 (0.55 to 0.64) for the composite respiratory endpoint, 0.35 (0.23 to 0.55) for acute pulmonary edema, 0.44 (0.18 to 1.05) for ARDS, 0.61 (0.56 to 0.66) for pneumonia, 0.49 (0.31 to 0.76) for respiratory failure, and 0.46 (0.41 to 0.51) for in-hospital death. Similar trends were found across individual SGLT2is, subgroup analyses of age, sex, history of comorbidities
Association of adverse respiratory events with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors among patients with type 2 diabetes in South Korea: a nationwide cohort study - BMC MedicineBackground Impaired respiratory function remains underrecognized in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D), despite common pulmonary impairment. Meanwhile, there is little data available on the respiratory effects of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i). Hence, we examined the association between SGLT2i use and the risk of adverse respiratory events in a real-world setting. Methods We conducted a population-based, nationwide cohort study using an active-comparator new-user design and nationwide claims data of South Korea from January 2015 to December 2020. Among individuals aged 18 years or older, propensity score matching was done to match each new user of SGLT2is with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4is), with patients followed up according to an as-treated definition. The primary outcome was respiratory events, a composite endpoint of acute pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), pneumonia, and respiratory failure. Secondary outcomes were the individual components of the primary outcome and in-hospital death. Cox models were used to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs. Results Of 205,534 patient pairs in the propensity score matched cohort, the mean age of the entire cohort was 53.8 years and 59% were men, with a median follow-up of 0.66 years; all baseline covariates achieved balance between the two groups. Incidence rates for overall respiratory events were 4.54 and 7.54 per 1000 person-years among SGLT2i and DPP4i users, respectively, corresponding to a rate difference of 3 less events per 1000 person-years (95% CI − 3.44 to − 2.55). HRs (95% CIs) were 0.60 (0.55 to 0.64) for the composite respiratory endpoint, 0.35 (0.23 to 0.55) for acute pulmonary edema, 0.44 (0.18 to 1.05) for ARDS, 0.61 (0.56 to 0.66) for pneumonia, 0.49 (0.31 to 0.76) for respiratory failure, and 0.46 (0.41 to 0.51) for in-hospital death. Similar trends were found across individual SGLT2is, subgroup analyses of age, sex, history of comorbidities
Read more »
 Inflammation and neuronal gene expression changes differ in early versus late chronic traumatic encephalopathy brain - BMC Medical GenomicsBackground Our understanding of the molecular underpinnings of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) and its associated pathology in post-mortem brain is incomplete. Factors including years of play and genetic risk variants influence the extent of tau pathology associated with disease expression, but how these factors affect gene expression, and whether those effects are consistent across the development of disease, is unknown. Methods To address these questions, we conducted an analysis of the largest post-mortem brain CTE mRNASeq whole-transcriptome dataset available to date. We examined the genes and biological processes associated with disease by comparing individuals with CTE with control individuals with a history of repetitive head impacts that lack CTE pathology. We then identified genes and biological processes associated with total years of play as a measure of exposure, amount of tau pathology present at time of death, and the presence of APOE and TMEM106B risk variants. Samples were stratified into low and high pathology groups based on McKee CTE staging criteria to model early versus late changes in response to exposure, and the relative effects associated with these factors were compared between these groups. Results Substantial gene expression changes were associated with severe disease for most of these factors, primarily implicating diverse, strongly involved neuroinflammatory and neuroimmune processes. In contrast, low pathology groups had many fewer genes and processes implicated and show striking differences for some factors when compared with severe disease. Specifically, gene expression associated with amount of tau pathology showed a nearly perfect inverse relationship when compared between these two groups. Conclusions Together, these results suggest the early CTE disease process may be mechanistically different than what occurs in late stages, that total years of play and tau pathology influence disease expression differently, and that rela
Inflammation and neuronal gene expression changes differ in early versus late chronic traumatic encephalopathy brain - BMC Medical GenomicsBackground Our understanding of the molecular underpinnings of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) and its associated pathology in post-mortem brain is incomplete. Factors including years of play and genetic risk variants influence the extent of tau pathology associated with disease expression, but how these factors affect gene expression, and whether those effects are consistent across the development of disease, is unknown. Methods To address these questions, we conducted an analysis of the largest post-mortem brain CTE mRNASeq whole-transcriptome dataset available to date. We examined the genes and biological processes associated with disease by comparing individuals with CTE with control individuals with a history of repetitive head impacts that lack CTE pathology. We then identified genes and biological processes associated with total years of play as a measure of exposure, amount of tau pathology present at time of death, and the presence of APOE and TMEM106B risk variants. Samples were stratified into low and high pathology groups based on McKee CTE staging criteria to model early versus late changes in response to exposure, and the relative effects associated with these factors were compared between these groups. Results Substantial gene expression changes were associated with severe disease for most of these factors, primarily implicating diverse, strongly involved neuroinflammatory and neuroimmune processes. In contrast, low pathology groups had many fewer genes and processes implicated and show striking differences for some factors when compared with severe disease. Specifically, gene expression associated with amount of tau pathology showed a nearly perfect inverse relationship when compared between these two groups. Conclusions Together, these results suggest the early CTE disease process may be mechanistically different than what occurs in late stages, that total years of play and tau pathology influence disease expression differently, and that rela
Read more »
 Efficacy and safety of topical 0.1% cannabidiol for managing recurrent aphthous ulcers: a randomized controlled trial - BMC Complementary Medicine and TherapiesBackground Although topical steroids constitute the first-line therapy for recurrent aphthous ulcers (RAUs), their long-term use often leads to candidiasis. Although cannabidiol (CBD) can be an alternative for pharmacologically managing RAUs due to its analgesic and anti-inflammatory in vivo effects, there is a lack of clinical and safety trials concerning its use. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical safety and efficacy of topical 0.1% CBD for managing RAU. Methods A CBD patch test was performed on 100 healthy subjects. CBD was applied on the normal oral mucosa of 50 healthy subjects 3 times/day for 7 days. Oral examination, vital signs, and blood tests were performed pre- and post-CBD use. Another 69 RAU subjects randomly received one of three topical interventions: 0.1% CBD, 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide (TA), or placebo. These were applied on the ulcers 3 times/day for 7 days. The ulcer and erythematous size were measured on day 0, 2, 5, and 7. Pain ratings were recorded daily. The subjects rated their satisfaction with the intervention and completed a quality-of-life questionnaire (OHIP-14). Results None of the subjects exhibited allergic reactions or side effects. Their vital signs and blood parameters were stable before and after the 7-day CBD intervention. CBD and TA significantly reduced ulcer size more than placebo at all time points. The erythematous size reduction was higher in the CBD intervention than the placebo on day 2, while TA reduced the erythematous size at all time points. The pain score in the CBD group was lower compared with placebo on day 5, whereas TA reduced pain more than placebo on day 4, 5, and 7. The subjects receiving CBD reported higher satisfaction than placebo. However, the OHIP-14 scores were comparable among the interventions. Conclusions Topical 0.1% CBD reduced ulcer size and accelerated ulcer healing without side effects. CBD exerted anti-inflammatory effects in the early stage and an analgesic effect in the late
Efficacy and safety of topical 0.1% cannabidiol for managing recurrent aphthous ulcers: a randomized controlled trial - BMC Complementary Medicine and TherapiesBackground Although topical steroids constitute the first-line therapy for recurrent aphthous ulcers (RAUs), their long-term use often leads to candidiasis. Although cannabidiol (CBD) can be an alternative for pharmacologically managing RAUs due to its analgesic and anti-inflammatory in vivo effects, there is a lack of clinical and safety trials concerning its use. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical safety and efficacy of topical 0.1% CBD for managing RAU. Methods A CBD patch test was performed on 100 healthy subjects. CBD was applied on the normal oral mucosa of 50 healthy subjects 3 times/day for 7 days. Oral examination, vital signs, and blood tests were performed pre- and post-CBD use. Another 69 RAU subjects randomly received one of three topical interventions: 0.1% CBD, 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide (TA), or placebo. These were applied on the ulcers 3 times/day for 7 days. The ulcer and erythematous size were measured on day 0, 2, 5, and 7. Pain ratings were recorded daily. The subjects rated their satisfaction with the intervention and completed a quality-of-life questionnaire (OHIP-14). Results None of the subjects exhibited allergic reactions or side effects. Their vital signs and blood parameters were stable before and after the 7-day CBD intervention. CBD and TA significantly reduced ulcer size more than placebo at all time points. The erythematous size reduction was higher in the CBD intervention than the placebo on day 2, while TA reduced the erythematous size at all time points. The pain score in the CBD group was lower compared with placebo on day 5, whereas TA reduced pain more than placebo on day 4, 5, and 7. The subjects receiving CBD reported higher satisfaction than placebo. However, the OHIP-14 scores were comparable among the interventions. Conclusions Topical 0.1% CBD reduced ulcer size and accelerated ulcer healing without side effects. CBD exerted anti-inflammatory effects in the early stage and an analgesic effect in the late
Read more »
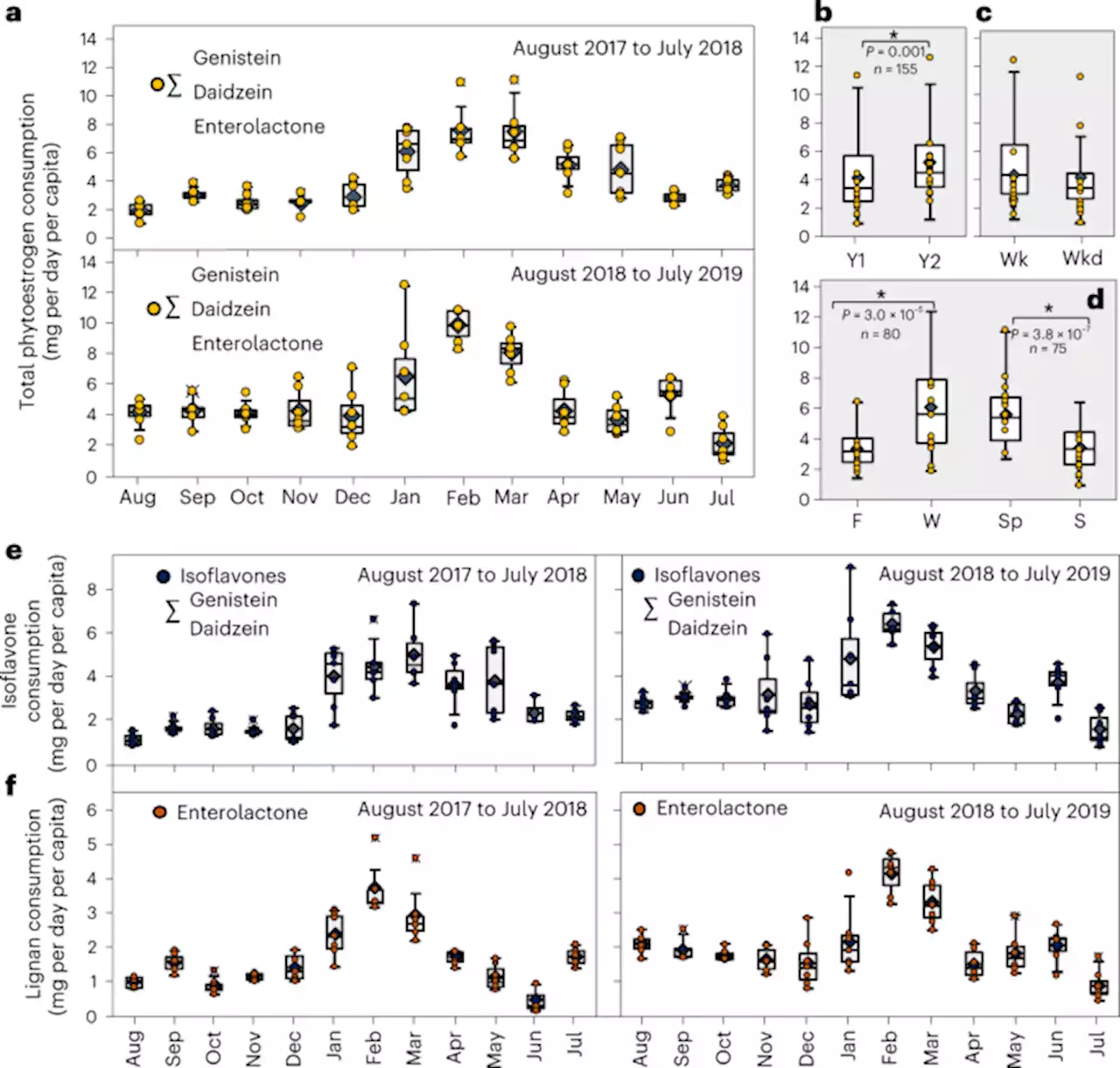 Integrated multiomic wastewater-based epidemiology can elucidate population-level dietary behaviour and inform public health nutrition assessments - Nature FoodSelf-reported data can introduce recall bias into population-level nutritional assessments. Wastewater analyses combining metabolomic and genomic techniques can inform nutritional assessments at the population scale and support public health nutrition.
Integrated multiomic wastewater-based epidemiology can elucidate population-level dietary behaviour and inform public health nutrition assessments - Nature FoodSelf-reported data can introduce recall bias into population-level nutritional assessments. Wastewater analyses combining metabolomic and genomic techniques can inform nutritional assessments at the population scale and support public health nutrition.
Read more »
