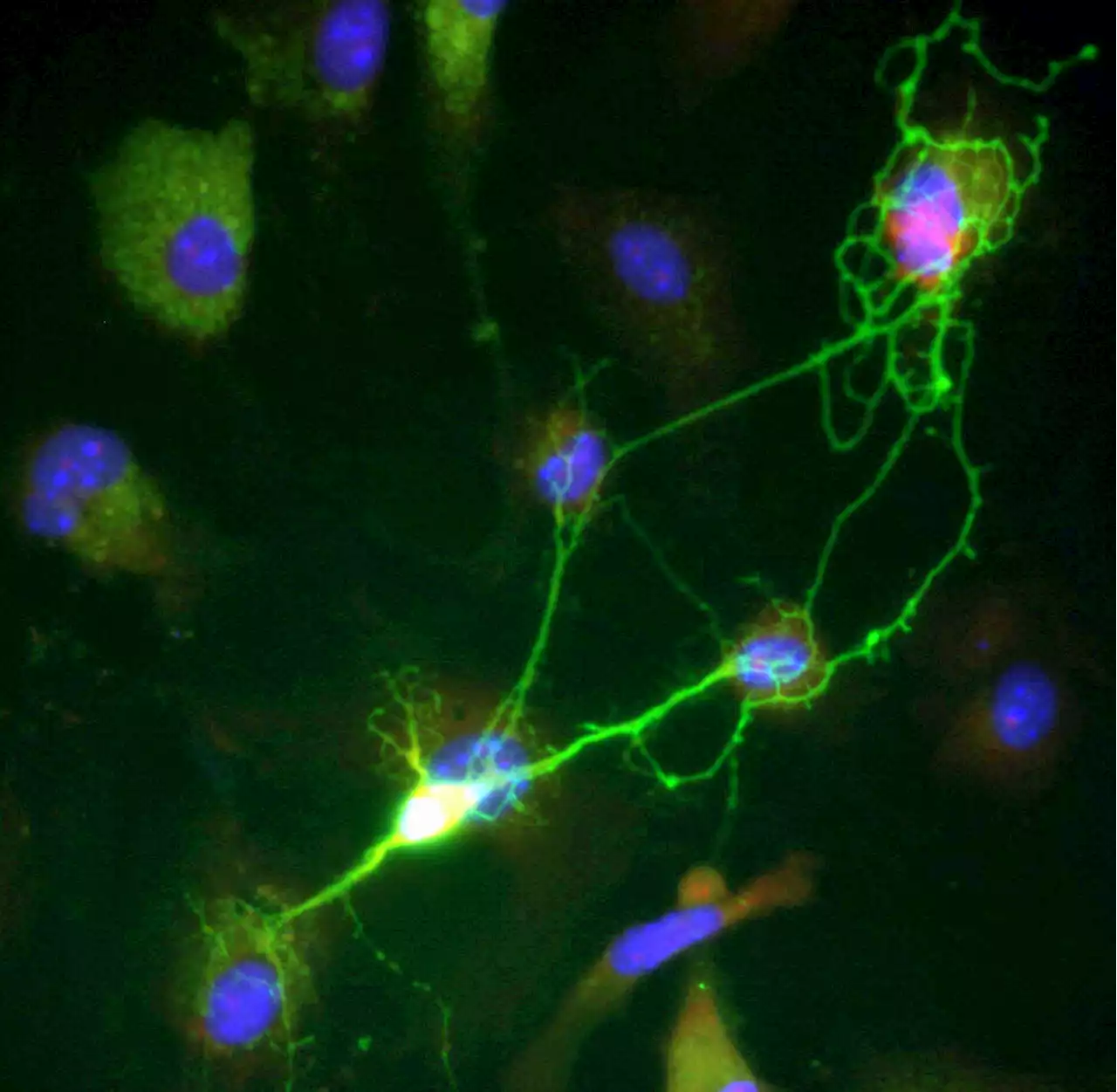
A research team from University of Lausanne (UNIL) and the Wyss Center, has discovered a new type of cell essential for brain function. Hybrid in composition and function, in between the two types of brain cells known so far—the neurons and the glial cells—these cells of a new order are present in several brain regions in mice and humans.
, intimately surround synapses, the points of contact where neurotransmitters are released to transmit information between neurons.
This is why neuroscientists have long suggested that astrocytes may have an active role in synaptic transmission and participate in information processing. However, the studies conducted to date to demonstrate this have suffered from conflicting results and have not reached a definitive scientific consensus yet.
"The precision allowed by single-cell transcriptomics approaches enabled us to demonstrate the presence in cells with astrocytic profile of transcripts of the vesicular proteins, VGLUT, in charge of filling neuronal vesicles specific for glutamate release. These transcripts were found in cells from mice, and are apparently preserved in human cells.
"We have identified a subgroup of astrocytes responding to selective stimulations with rapid glutamate release, which occurred in spatially delimited areas of these cells reminiscent of synapses," says Andrea Volterra, honorary professor at UNIL and visiting faculty at the Wyss Center, co-director of the study.
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Glasgow University's Gilbert Scott Building among 'most beautiful' in EuropeGlasgow University's Gilbert Scott Building has been listed among some of the most 'beautiful' universities in Europe with the University of St. Andrews also making the list.
Glasgow University's Gilbert Scott Building among 'most beautiful' in EuropeGlasgow University's Gilbert Scott Building has been listed among some of the most 'beautiful' universities in Europe with the University of St. Andrews also making the list.
Read more »
 Bangor University scientists design fuel for nuclear reactors on the moonA team at a university in north Wales has been conducting research which they say will make space travel safer and more efficient.
Bangor University scientists design fuel for nuclear reactors on the moonA team at a university in north Wales has been conducting research which they say will make space travel safer and more efficient.
Read more »
 Almost half of students do not think university is worth the moneyNearly three quarters (72 per cent) said they were shocked by how much university now costs
Almost half of students do not think university is worth the moneyNearly three quarters (72 per cent) said they were shocked by how much university now costs
Read more »
 Nearly half of students do not believe university is worth the costNearly three quarters (72 per cent) said they were shocked by how much university now costs
Nearly half of students do not believe university is worth the costNearly three quarters (72 per cent) said they were shocked by how much university now costs
Read more »
 Study examines role of religion in substance use services, finds it's often located in racially diverse communitiesPeople have turned to religion and spirituality to deal with crises and critical needs for centuries. Yet little is known how religion plays a role in substance use care. A new publication from the University of Kansas and Georgetown University explored the religious orientation of facilities within the substance use and addiction system of care throughout the Kansas City region, the religiousness of services, where the services are located and differences in services offered.
Study examines role of religion in substance use services, finds it's often located in racially diverse communitiesPeople have turned to religion and spirituality to deal with crises and critical needs for centuries. Yet little is known how religion plays a role in substance use care. A new publication from the University of Kansas and Georgetown University explored the religious orientation of facilities within the substance use and addiction system of care throughout the Kansas City region, the religiousness of services, where the services are located and differences in services offered.
Read more »
 Hope for new therapy to stop advanced skin cancerResearchers at St George's, University of London have discovered a technique that can kill skin cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells. The findings are published in the journal Biology Open.
Hope for new therapy to stop advanced skin cancerResearchers at St George's, University of London have discovered a technique that can kill skin cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells. The findings are published in the journal Biology Open.
Read more »