Enzyme inhibitor slows tumor growth
]. Primary B-cells were grown in RPMI 1640 with 10% FCS, 50 µM β-mercaptoethanol, 10 mM HEPES and 0.5% gentamicin. Activation of primary B-cells was induced by the addition of 10 µg/ml LPS . Ramos cells were authenticated by Eurofins Genomics using PCR-single-locus-technology with 21 independent PCR-systems. M-100 was dissolved to a 10 mM stock solution with DMSO and diluted to a concentration of 100 µM with PBS. M-100 is registered under patent number WO2016020369 A1.
Beads were washed three times in lysis buffer after incubation, resuspended in 2x Laemmli buffer to a final 1x concentration, and boiled for 5 min at 95 °C.PLA was performed using Duolink In Situ PLA Reagents Red according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Ramos cells were attached to coverslips with 0.1% poly-L-lysine for 1 h at RT. Cells were permeabilized, fixed with methanol for 10 min at −20 °C, blocked with Duolink blocking solution, and incubated with primary antibodies.
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Frontiers | Targeting bladder urothelial carcinoma with pHLIP-ICG and inhibition of urothelial cancer cell proliferation by pHLIP-amanitinAcidity is a useful biomarker for the targeting of metabolically active cells in tumors. pH Low Insertion Peptides (pHLIPs) sense the pH at the surfaces of tumor cells and can facilitate intracellular delivery of cell-permeable and cell-impermeable cargo molecules. In this study we have shown the targeting of malignant lesions in human bladders by fluorescent pHLIP agents, intracellular delivery of amanitin toxin by pHLIP for the inhibition of urothelial cancer cell proliferation, and enhanced potency of pHLIP-amanitin for cancer cells with 17p loss, a mutation frequently present in urothelial cancers. Twenty-eight ex-vivo bladder specimens, from patients undergoing robotic assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy for bladder cancer, were treated via intravesical incubation for 15-60 minutes with pHLIP conjugated to indocyanine green (ICG) or IR-800 near infrared fluorescent (NIRF) dyes at concentrations of 4-8 M. White light cystoscopy identified 47/58 (81%) and NIRF pHLIP cystoscopy identified 57/58 (98.3%) of malignant lesions of different subtypes and stages selected for histopathological processing. pHLIP NIRF imaging improved diagnosis by 17.3% (p | 0.05). All carcinoma-in-situ cases missed by white light cystoscopy were targeted by pHLIP agents and were diagnosed by NIRF imaging. We also investigated the interactions of pHLIP-amanitin with urothelial cancer cells of different grades. pHLIP-amanitin produced concentration- and pH-dependent inhibition of the proliferation of urothelial cancer cells treated for 2 hrs at concentrations up to 4 M. A 3-4x enhanced cytotoxicity of pHLIP-amanitin was observed for cells with a 17p loss after 2 hrs of treatment at pH6. Potentially, pHLIP technology may improve the management of urothelial cancers, including imaging of malignant lesions using pHLIP-ICG for diagnosis and surgery, and the use of pHLIP-amanitin for treatment of superficial bladder cancers via intravesical instillation.
Frontiers | Targeting bladder urothelial carcinoma with pHLIP-ICG and inhibition of urothelial cancer cell proliferation by pHLIP-amanitinAcidity is a useful biomarker for the targeting of metabolically active cells in tumors. pH Low Insertion Peptides (pHLIPs) sense the pH at the surfaces of tumor cells and can facilitate intracellular delivery of cell-permeable and cell-impermeable cargo molecules. In this study we have shown the targeting of malignant lesions in human bladders by fluorescent pHLIP agents, intracellular delivery of amanitin toxin by pHLIP for the inhibition of urothelial cancer cell proliferation, and enhanced potency of pHLIP-amanitin for cancer cells with 17p loss, a mutation frequently present in urothelial cancers. Twenty-eight ex-vivo bladder specimens, from patients undergoing robotic assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy for bladder cancer, were treated via intravesical incubation for 15-60 minutes with pHLIP conjugated to indocyanine green (ICG) or IR-800 near infrared fluorescent (NIRF) dyes at concentrations of 4-8 M. White light cystoscopy identified 47/58 (81%) and NIRF pHLIP cystoscopy identified 57/58 (98.3%) of malignant lesions of different subtypes and stages selected for histopathological processing. pHLIP NIRF imaging improved diagnosis by 17.3% (p | 0.05). All carcinoma-in-situ cases missed by white light cystoscopy were targeted by pHLIP agents and were diagnosed by NIRF imaging. We also investigated the interactions of pHLIP-amanitin with urothelial cancer cells of different grades. pHLIP-amanitin produced concentration- and pH-dependent inhibition of the proliferation of urothelial cancer cells treated for 2 hrs at concentrations up to 4 M. A 3-4x enhanced cytotoxicity of pHLIP-amanitin was observed for cells with a 17p loss after 2 hrs of treatment at pH6. Potentially, pHLIP technology may improve the management of urothelial cancers, including imaging of malignant lesions using pHLIP-ICG for diagnosis and surgery, and the use of pHLIP-amanitin for treatment of superficial bladder cancers via intravesical instillation.
Read more »
 New Strategy To Help Chitosan Nanocrystals Target CellsAn article published in the journal Carbohydrate Polymers presented a new methodology to functionalize the chitosan nanocrystals with peptides and amino acids via solid phase peptide synthesis.
New Strategy To Help Chitosan Nanocrystals Target CellsAn article published in the journal Carbohydrate Polymers presented a new methodology to functionalize the chitosan nanocrystals with peptides and amino acids via solid phase peptide synthesis.
Read more »
 Transient cell-in-cell formation underlies tumor relapse and resistance to immunotherapyTumors escape killing by the immune system through generating transient spatial cell-in-cell structures that are impenetrable to cytotoxic compounds including lytic granules and chemotherapy.
Transient cell-in-cell formation underlies tumor relapse and resistance to immunotherapyTumors escape killing by the immune system through generating transient spatial cell-in-cell structures that are impenetrable to cytotoxic compounds including lytic granules and chemotherapy.
Read more »
 Zika Virus Strains and Dengue Virus Induce Distinct Proteomic Changes in Neural Stem Cells and Neurospheres - Molecular NeurobiologyBrain abnormalities and congenital malformations have been linked to the circulating strain of Zika virus (ZIKV) in Brazil since 2016 during the microcephaly outbreak; however, the molecular mechanisms behind several of these alterations and differential viral molecular targets have not been fully elucidated. Here we explore the proteomic alterations induced by ZIKV by comparing the Brazilian (Br ZIKV) and the African (MR766) viral strains, in addition to comparing them to the molecular responses to the Dengue virus type 2 (DENV). Neural stem cells (NSCs) derived from induced pluripotent stem (iPSCs) were cultured both as monolayers and in suspension (resulting in neurospheres), which were then infected with ZIKV (Br ZIKV or ZIKV MR766) or DENV to assess alterations within neural cells. Large-scale proteomic analyses allowed the comparison not only between viral strains but also regarding the two- and three-dimensional cellular models of neural cells derived from iPSCs, and the effects on their interaction. Altered pathways and biological processes were observed related to cell death, cell cycle dysregulation, and neurogenesis. These results reinforce already published data and provide further information regarding the biological alterations induced by ZIKV and DENV in neural cells.
Zika Virus Strains and Dengue Virus Induce Distinct Proteomic Changes in Neural Stem Cells and Neurospheres - Molecular NeurobiologyBrain abnormalities and congenital malformations have been linked to the circulating strain of Zika virus (ZIKV) in Brazil since 2016 during the microcephaly outbreak; however, the molecular mechanisms behind several of these alterations and differential viral molecular targets have not been fully elucidated. Here we explore the proteomic alterations induced by ZIKV by comparing the Brazilian (Br ZIKV) and the African (MR766) viral strains, in addition to comparing them to the molecular responses to the Dengue virus type 2 (DENV). Neural stem cells (NSCs) derived from induced pluripotent stem (iPSCs) were cultured both as monolayers and in suspension (resulting in neurospheres), which were then infected with ZIKV (Br ZIKV or ZIKV MR766) or DENV to assess alterations within neural cells. Large-scale proteomic analyses allowed the comparison not only between viral strains but also regarding the two- and three-dimensional cellular models of neural cells derived from iPSCs, and the effects on their interaction. Altered pathways and biological processes were observed related to cell death, cell cycle dysregulation, and neurogenesis. These results reinforce already published data and provide further information regarding the biological alterations induced by ZIKV and DENV in neural cells.
Read more »
JCI Insight - MCP-1/CCR2 axis inhibition sensitizes the brain microenvironment against melanoma brain metastasis progression
Read more »
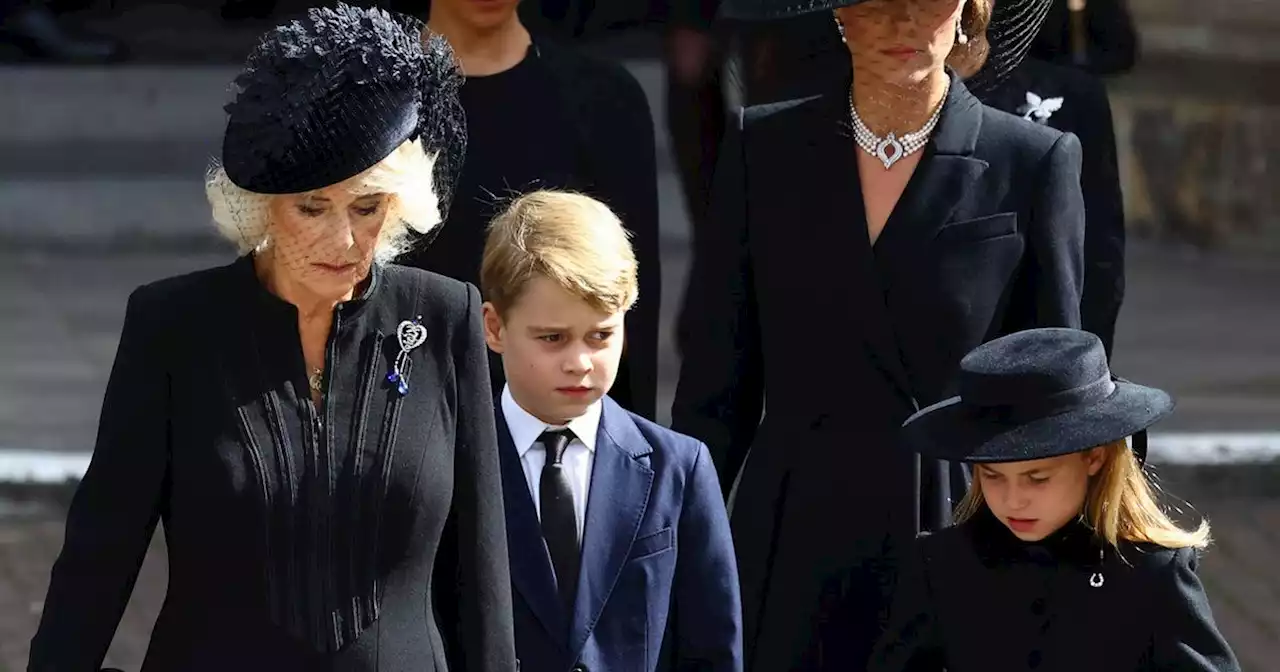 Camilla's frustrated words to Kate over Charlotte and George 'disagreement'Queen consort Camilla appeared to get frustrated over the antics of Princess Charlotte and Prince George at the Queen's funeral after a playful interaction
Camilla's frustrated words to Kate over Charlotte and George 'disagreement'Queen consort Camilla appeared to get frustrated over the antics of Princess Charlotte and Prince George at the Queen's funeral after a playful interaction
Read more »
