Researchers found that healthy plant-based diets reduce the risk of gout, while unhealthy plant-based diets increase the risk, especially among women.
By Dr. Liji Thomas, MDMay 26 2024Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. A recent study published in JAMA explores the potential benefits of a plant-based diet on gout risk.
Certain food products, including alcohol, red meat, fish, and sugary drinks, have been shown to increase the risk of gout. Conversely, skim dairy products, coffee, certain vegetables, and ascorbic acid can reduce the risk of gout. The study aimed to measure mean exposure to an overall plant-based diet index , healthy PDI , and unhealthy PDI . These indices were calculated based on 18 food groups determined using a food frequency questionnaire.
The risk of gout increased by 17% in the hPDI cohort from the highest to the least quintile, while it was nearly 20% lower from the highest to the least quintile in the uPDI cohort. Whole grains reduced the risk of gout by 7% per serving, tea and coffee by 5% per serving, and dairy products by 15% per serving. Conversely, fruit juice and sugary drinks increased the risk of gout by 6%, whereas vegetable oils increased the risk of gout by 16% per serving. The inverse association between whole grains and gout risk was reported in the current study for the first time.
Fish is purine-rich, which can increase serum uric acid levels and, as a result, increase an individual’s vulnerability to gout. The reduction of gout risk with sweets and desserts and the lack of an association with refined grains requires further exploration to understand the mechanisms responsible for this association.
Alcohol Ascorbic Acid Cardiometabolic Coffee Diet Fish Food Meat Mediterranean Diet Mental Health Mortality Vegetables
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers study indicators of coronary obstructions in women with established coronary artery diseaseResearchers in medicine have been studying the composition of biochemical markers to determine correlations between during health and disease for several decades. The data helps health care professionals to accurately diagnose and treat diseases, some of which are life threatening.
Researchers study indicators of coronary obstructions in women with established coronary artery diseaseResearchers in medicine have been studying the composition of biochemical markers to determine correlations between during health and disease for several decades. The data helps health care professionals to accurately diagnose and treat diseases, some of which are life threatening.
Read more »
 Researchers advocate for structured framework to study the benefits of exercise training in multiple sclerosis rehabA team of experts in multiple sclerosis (MS) research recommends a structured approach to the study of mechanisms of exercise training for improving outcomes for multiple sclerosis (MS).
Researchers advocate for structured framework to study the benefits of exercise training in multiple sclerosis rehabA team of experts in multiple sclerosis (MS) research recommends a structured approach to the study of mechanisms of exercise training for improving outcomes for multiple sclerosis (MS).
Read more »
 Q&A: Researchers discusses 25-year study that shows mothers' empathy for teens may predict teens' empathyA new Child Development study from researchers at the University of Virginia provides the first long-term, longitudinal evidence for the transmission of empathic care across three generations: from mother to teen to child.
Q&A: Researchers discusses 25-year study that shows mothers' empathy for teens may predict teens' empathyA new Child Development study from researchers at the University of Virginia provides the first long-term, longitudinal evidence for the transmission of empathic care across three generations: from mother to teen to child.
Read more »
 Plant-based diets reduce cancer and heart disease risks, study showsStudy reveals that plant-based diets significantly reduce the risks of cancer and cardiometabolic diseases while improving overall health markers.
Plant-based diets reduce cancer and heart disease risks, study showsStudy reveals that plant-based diets significantly reduce the risks of cancer and cardiometabolic diseases while improving overall health markers.
Read more »
 Researchers trace the evolution of key plant protein in lignin synthesisScientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered that a protein responsible for the synthesis of a key plant material evolved much earlier than suspected.
Researchers trace the evolution of key plant protein in lignin synthesisScientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered that a protein responsible for the synthesis of a key plant material evolved much earlier than suspected.
Read more »
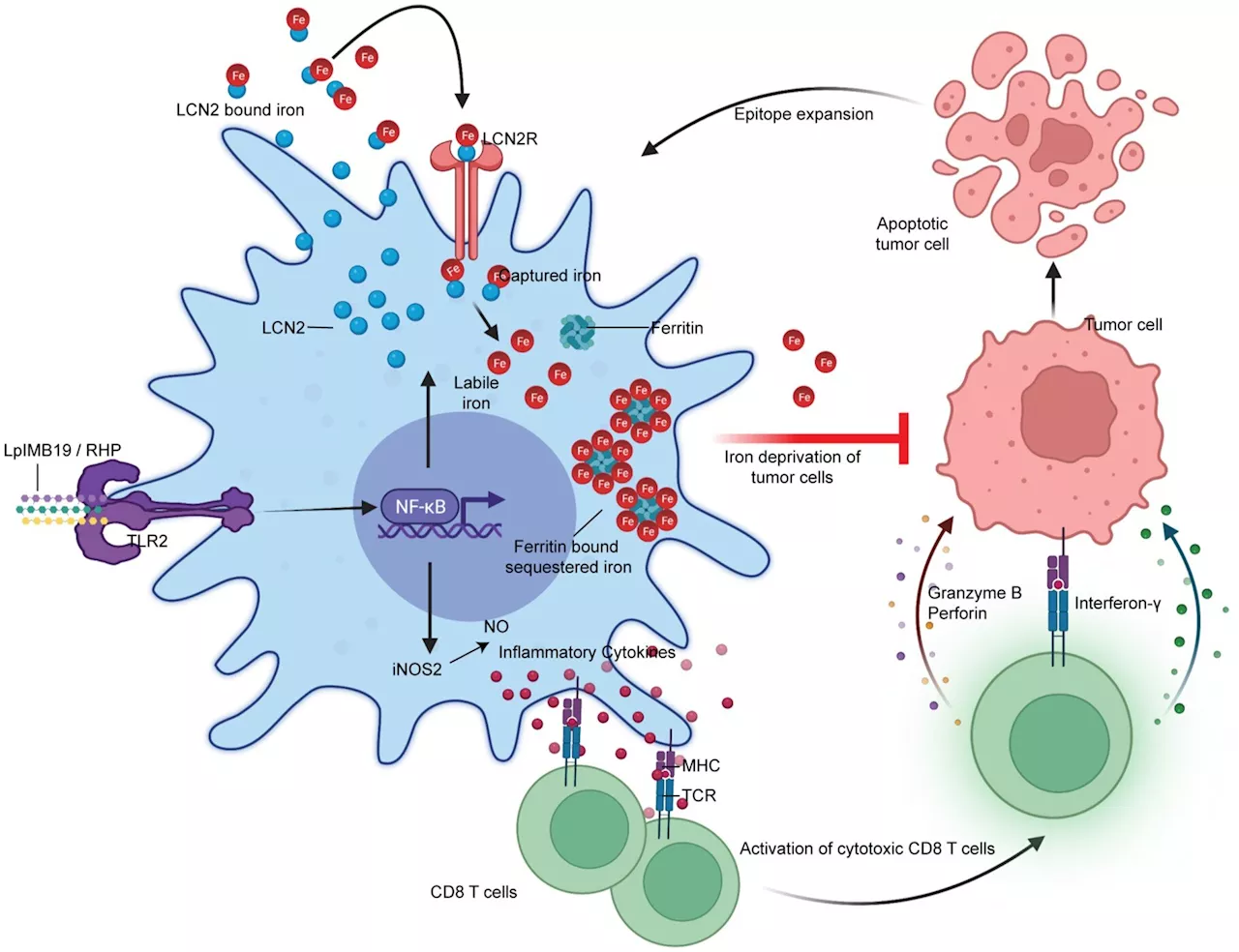 Researchers make strides in microbiome-based cancer therapies via iron deprivation in the tumor microenvironmentA team from POSTECH and ImmunoBiome has made a potential breakthrough in the fight against cancer. Their research, published in the May issue of Nature Immunology, explores a dietary-derived bacterial strain, IMB001. This strain induces 'nutritional immunity' to boost anti-tumor responses.
Researchers make strides in microbiome-based cancer therapies via iron deprivation in the tumor microenvironmentA team from POSTECH and ImmunoBiome has made a potential breakthrough in the fight against cancer. Their research, published in the May issue of Nature Immunology, explores a dietary-derived bacterial strain, IMB001. This strain induces 'nutritional immunity' to boost anti-tumor responses.
Read more »