A research paper published in the journal Cell Metabolism by the team of Prof. Liu Qiang at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) reveals the critical role of glutamate tRNA fragments in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease.
Study reveals key role of glutamate tRNA fragments in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease retrieved 13 May 2024 from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-05-reveals-key-role-glutamate-trna.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Medicine Research Health Research News Health Research Health Science Medicine Science
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
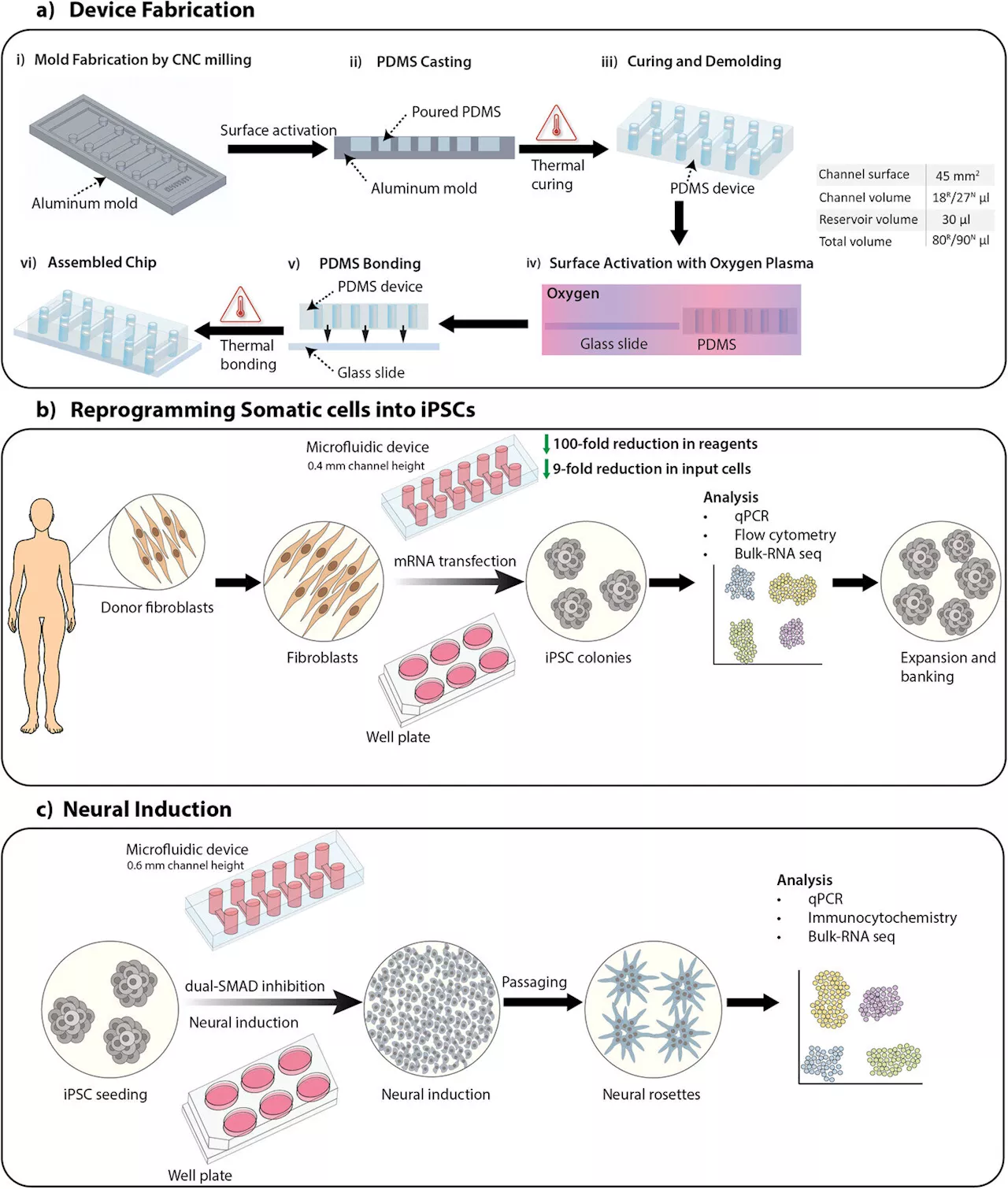 New device improves stem cell generation and chance for accessible Alzheimer's cell therapyResearchers in Sweden say they have improved on a technique for converting regular skin cells into neural stem cells—an advance that they say helps close the gap for accessible personalized cell-based therapies for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
New device improves stem cell generation and chance for accessible Alzheimer's cell therapyResearchers in Sweden say they have improved on a technique for converting regular skin cells into neural stem cells—an advance that they say helps close the gap for accessible personalized cell-based therapies for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Read more »
 Innovative microscopy demystifies metabolism of Alzheimer'sAlzheimer's disease causes significant problems with memory, thinking and behavior and is the most common form of dementia, affecting more than 50 million people around the world each year. This number is expected to triple by the year 2050.
Innovative microscopy demystifies metabolism of Alzheimer'sAlzheimer's disease causes significant problems with memory, thinking and behavior and is the most common form of dementia, affecting more than 50 million people around the world each year. This number is expected to triple by the year 2050.
Read more »
 Study elucidates how energy metabolism is regulated at cellular levelAn article published in The FASEB Journal describes a Brazilian study analyzing the correlation between two key energy metabolism regulation processes: the absorption and release of calcium ions by mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for cells; and autophagy induced by calorie restriction.
Study elucidates how energy metabolism is regulated at cellular levelAn article published in The FASEB Journal describes a Brazilian study analyzing the correlation between two key energy metabolism regulation processes: the absorption and release of calcium ions by mitochondria, the organelles that generate energy for cells; and autophagy induced by calorie restriction.
Read more »
 Study: Progression of herpesvirus infection remodels mitochondrial organization and metabolismResearchers at the University of Jyväskylä have found that herpesvirus infection modifies the structure and normal function of the mitochondria in the host cell. The new information could help to understand the interaction between herpesvirus and host cells and develop new viral treatments.
Study: Progression of herpesvirus infection remodels mitochondrial organization and metabolismResearchers at the University of Jyväskylä have found that herpesvirus infection modifies the structure and normal function of the mitochondria in the host cell. The new information could help to understand the interaction between herpesvirus and host cells and develop new viral treatments.
Read more »
 CD7 CAR T-cell therapy, stem-cell transplant beneficial for CD7-positive tumorsFor patients with relapsed or refractory CD7-positive leukemia or lymphoma, sequential CD7 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy followed by haploidentical hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is safe and effective, with remission seen for most patients, according to a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
CD7 CAR T-cell therapy, stem-cell transplant beneficial for CD7-positive tumorsFor patients with relapsed or refractory CD7-positive leukemia or lymphoma, sequential CD7 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy followed by haploidentical hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is safe and effective, with remission seen for most patients, according to a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Read more »
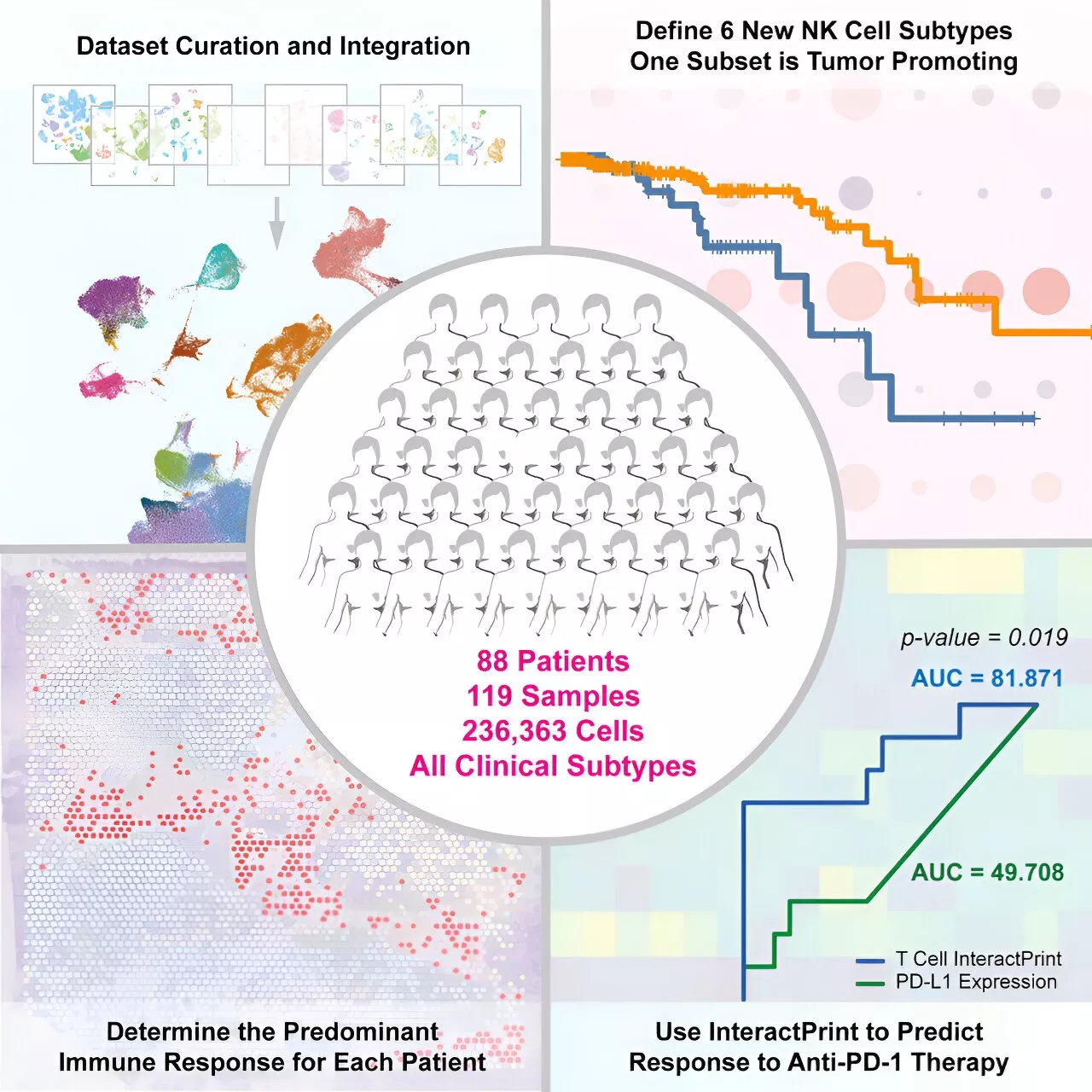 Cancer cell–immune cell interactions can predict immunotherapy responseBy examining which genes were turned on and off in a mix of cell types from breast cancer biopsies, a team led by UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers developed a tool that can accurately predict which patients with breast cancer will respond to immunotherapies.
Cancer cell–immune cell interactions can predict immunotherapy responseBy examining which genes were turned on and off in a mix of cell types from breast cancer biopsies, a team led by UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers developed a tool that can accurately predict which patients with breast cancer will respond to immunotherapies.
Read more »
