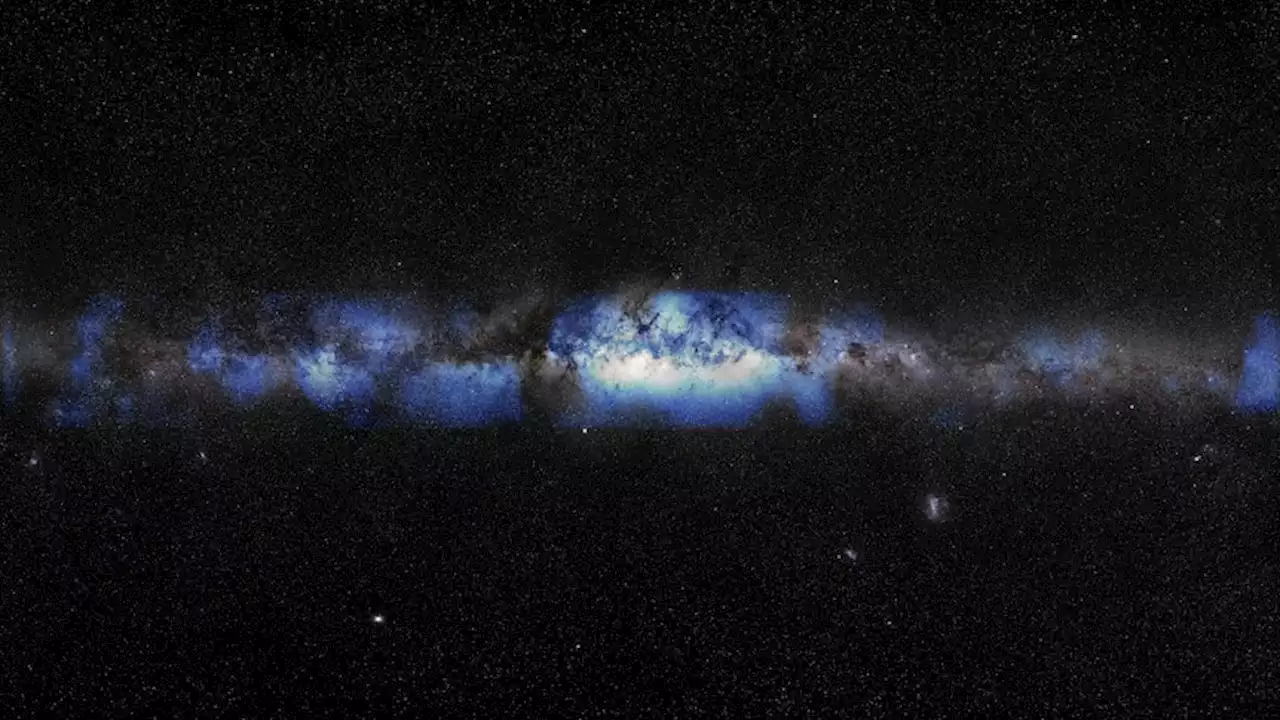
In a world-first, scientists say they produced an image of the Milky Way not based on electromagnetic radiation — light — but on ghostly subatomic particles called neutrinos.
abc.net.au/news/icecube-detector-finds-neutrinos-from-the-milky-way/102545654Human beings for millennia have gazed with awe at the vast torrent of stars — bright and dim — that comprise the Milky Way.They are high-energy 'ghost' particles that travel straight through matterOur home galaxy, however, is now being observed for the first time in a brand new way.
The study, which was published in the journal Science, said researchers detected high-energy neutrinos in pristine ice deep below Antarctica's surface, then traced their source back to locations in the Milky Way. This view differs fundamentally from what we can see with our own eyes or with instruments that measure other electromagnetic sources like radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma-rays.
The neutrinos were detected over a span of a decade at the IceCube Neutrino Observatory at a US scientific research station at the South Pole, using more than 5,000 sensors covering an area the size of a small mountain."This observation is groundbreaking. It established the galaxy as a neutrino source. Every future work will refer to this observation," said Georgia Tech physicist Ignacio Taboada, spokesperson for the IceCube research.
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Scientists find way to ‘hijack’ COVID virus to work ‘against itself’Southern Cross University Professor Jon Wardle says scientists in pre-clinical phases have found a way to tap into how the COVID virus replicates and “hijacks” the process to stop the virus from replicating and reproducing.
Scientists find way to ‘hijack’ COVID virus to work ‘against itself’Southern Cross University Professor Jon Wardle says scientists in pre-clinical phases have found a way to tap into how the COVID virus replicates and “hijacks” the process to stop the virus from replicating and reproducing.
Read more »
 'The most fun part of science': Scientists discover a planet that should not existAround 520 light years away lies a Jupiter sized planet that should have been destroyed. So how did it survive? It could have been like Tatooine from Star Wars.
'The most fun part of science': Scientists discover a planet that should not existAround 520 light years away lies a Jupiter sized planet that should have been destroyed. So how did it survive? It could have been like Tatooine from Star Wars.
Read more »
 Scientists make breakthrough in Multiple Sclerosis detectionMelbourne scientists have helped an international team forge a breakthrough in Multiple Sclerosis detection. They have located a genetic marker for the auto-immune disease, which can predict disease severity. It is the first time in 20 years they have been able to identify genes for severity and outcome, and professors believe it is very valuable information to eventually fight the disease.
Scientists make breakthrough in Multiple Sclerosis detectionMelbourne scientists have helped an international team forge a breakthrough in Multiple Sclerosis detection. They have located a genetic marker for the auto-immune disease, which can predict disease severity. It is the first time in 20 years they have been able to identify genes for severity and outcome, and professors believe it is very valuable information to eventually fight the disease.
Read more »
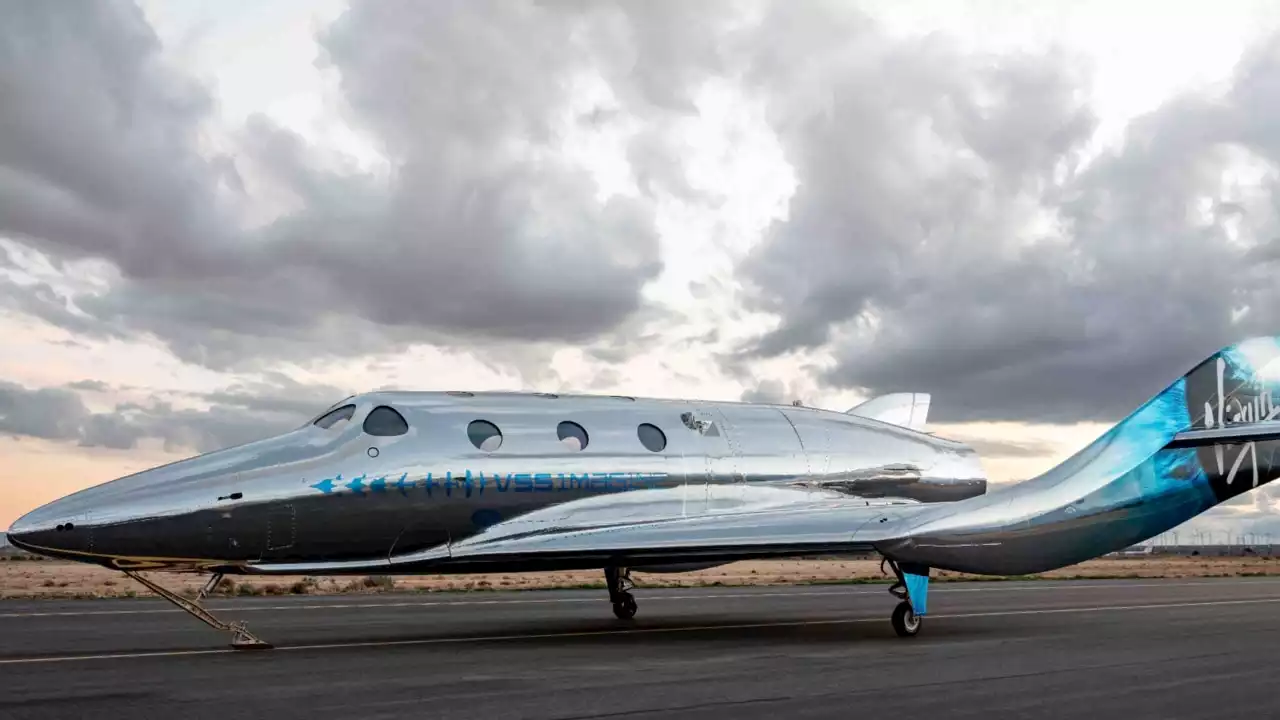 Virgin Galactic completes first commercial space flightVirgin Galactic has completed its first commercial flight into space by blasting a trio of Italian scientists 85 kilometres above the earth's surface. It paves the way for Virgin to take paying passengers, realising a 19-year dream for Sir Richard Branson's company.
Virgin Galactic completes first commercial space flightVirgin Galactic has completed its first commercial flight into space by blasting a trio of Italian scientists 85 kilometres above the earth's surface. It paves the way for Virgin to take paying passengers, realising a 19-year dream for Sir Richard Branson's company.
Read more »
 Ticketek ditches first come, first served method for 'fair' Taylor Swift presale queueTicketek has admitted the queue for presale tickets to Taylor Swift’s Australian leg of her international The Eras Tour was not first come, first served but maintained it was a fair and equal system.
Ticketek ditches first come, first served method for 'fair' Taylor Swift presale queueTicketek has admitted the queue for presale tickets to Taylor Swift’s Australian leg of her international The Eras Tour was not first come, first served but maintained it was a fair and equal system.
Read more »
