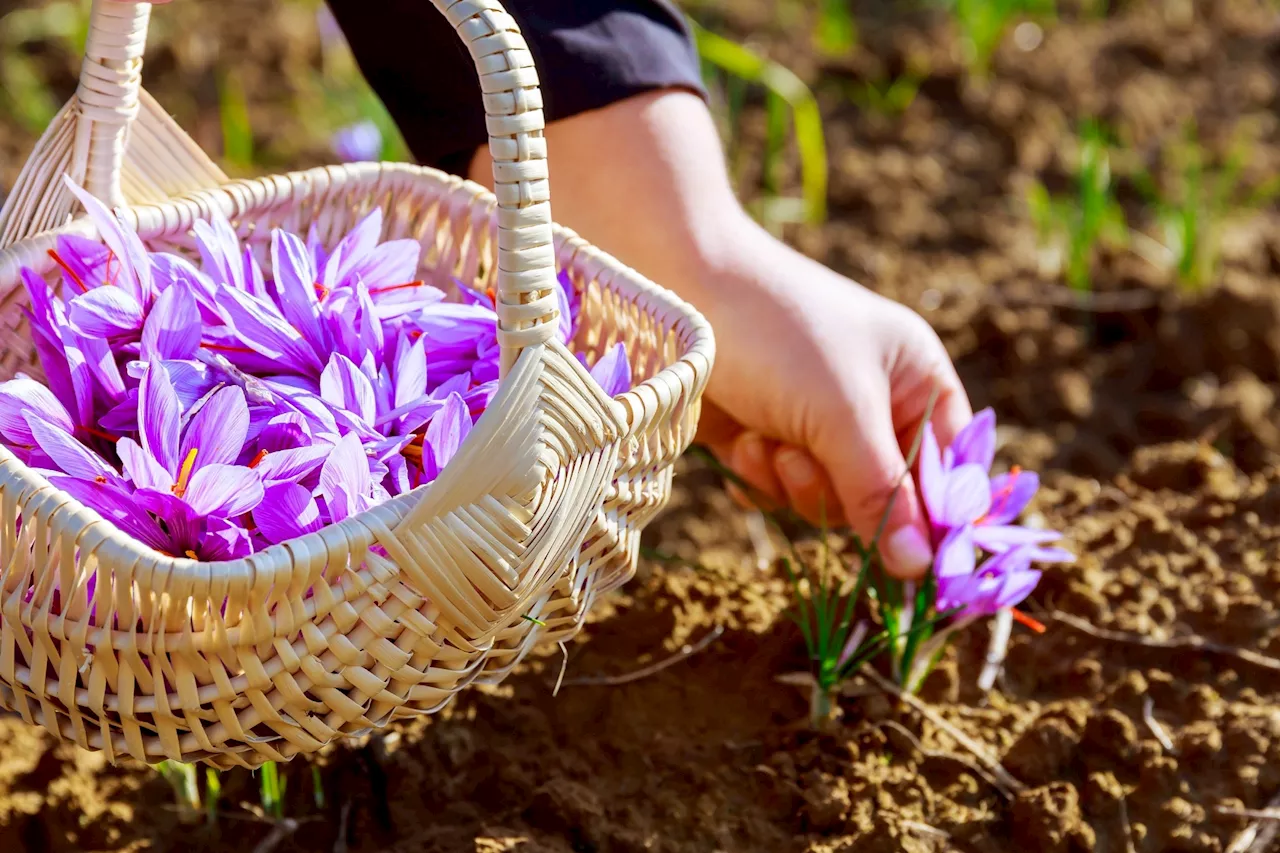
Review highlights saffron's potential in preventing and treating various human diseases through its bioactive compounds. Clinical and preclinical studies confirm saffron's benefits in conditions like maculopathy, depression, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer.
By Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta, Ph.D.Jul 21 2024 In a review article published in the journal Nutrients , the authors summarized the findings of existing studies investigating the significance of saffron and its by-products in preventing and treating a range of human diseases.
The authors of this review article have searched various scientific databases to identify studies that investigated the preventive and therapeutic potencies of saffron and its by-products. This review includes studies published in English between 1990 and 2024. Bioactive compounds found in saffron leaves include kaempferol and its derivatives, quercetin and its derivatives, luteolin and its derivatives, organic acids, and phenolic compounds.
A clinical trial involving patients with early degenerative maculopathy showed that daily saffron intake can improve visual acuity and slow disease progression. Carotenoids have also been reported to have a positive effect on retinal flicker sensitivity.Saffron's antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and serotonergic properties have made it a strong, natural antidepressant.
Crocin and crocetin have been found to inhibit amyloid-beta peptide aggression and delay synaptic loss, leading to neuroprotection against Alzheimer's disease-related cognitive deterioration.
Alzheimer's Disease Antifungal Anti-Inflammatory Antioxidant Anxiety Apoptosis Blood Cancer Cell Chronic Chronic Kidney Disease Clinical Trial Compound Cosmetics Depression Diabetes DNA Food Glucose Inflammation Kidney Kidney Disease Medicine Metabolic Syndrome Neurodegenerative Diseases Nutrients Oxidative Stress Quercetin Serotonin Spice Stress Syndrome
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Review finds no proven clinical benefit to strict salt restriction for patients with heart failureFor decades, it's been thought that people with heart failure should drastically reduce their dietary salt intake, but some studies have suggested that salt restriction could be harmful for these patients.
Review finds no proven clinical benefit to strict salt restriction for patients with heart failureFor decades, it's been thought that people with heart failure should drastically reduce their dietary salt intake, but some studies have suggested that salt restriction could be harmful for these patients.
Read more »
 Former church building in Hamilton put up for saleThe Saffron Hall in Windmill Road has been put on the market for offers over £110,000.
Former church building in Hamilton put up for saleThe Saffron Hall in Windmill Road has been put on the market for offers over £110,000.
Read more »
 AI model to improve clinical trial recruitment for eye diseaseA new artificial intelligence (AI) system that could significantly reduce the time and cost required to recruit clinical trial patients for an advanced form of age-related vision loss has been developed by a team led by UCL and Moorfields Eye Hospital researchers.
AI model to improve clinical trial recruitment for eye diseaseA new artificial intelligence (AI) system that could significantly reduce the time and cost required to recruit clinical trial patients for an advanced form of age-related vision loss has been developed by a team led by UCL and Moorfields Eye Hospital researchers.
Read more »
 First child receives skull-mounted epilepsy device in UK clinical trialOran, who had been having severe epileptic seizures for eight years and often needed resuscitation, was the first child in the UK to have this device implanted at Great Ormond Street Hospital in October 2023, when he was 12 years old.
First child receives skull-mounted epilepsy device in UK clinical trialOran, who had been having severe epileptic seizures for eight years and often needed resuscitation, was the first child in the UK to have this device implanted at Great Ormond Street Hospital in October 2023, when he was 12 years old.
Read more »
 Large integrative medicine center implements processes to measure and understand clinical effectivenessLed by a team of researchers at University Hospitals Connor Whole Health, a new study finds that collecting paper-based patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures of pain, anxiety, and stress is feasible—and that provider, operational, and clinical-level factors impact successful completion more so than patient factors.
Large integrative medicine center implements processes to measure and understand clinical effectivenessLed by a team of researchers at University Hospitals Connor Whole Health, a new study finds that collecting paper-based patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures of pain, anxiety, and stress is feasible—and that provider, operational, and clinical-level factors impact successful completion more so than patient factors.
Read more »
 Backward walking speed reserve assessment offers improved clinical screening for risks and decline in MS patientsWayne State University postdoctoral research fellows Patrick Monaghan, Ph.D., and Michael VanNostrand, Ph.D., along with Nora E. Fritz, Ph.D.
Backward walking speed reserve assessment offers improved clinical screening for risks and decline in MS patientsWayne State University postdoctoral research fellows Patrick Monaghan, Ph.D., and Michael VanNostrand, Ph.D., along with Nora E. Fritz, Ph.D.
Read more »
