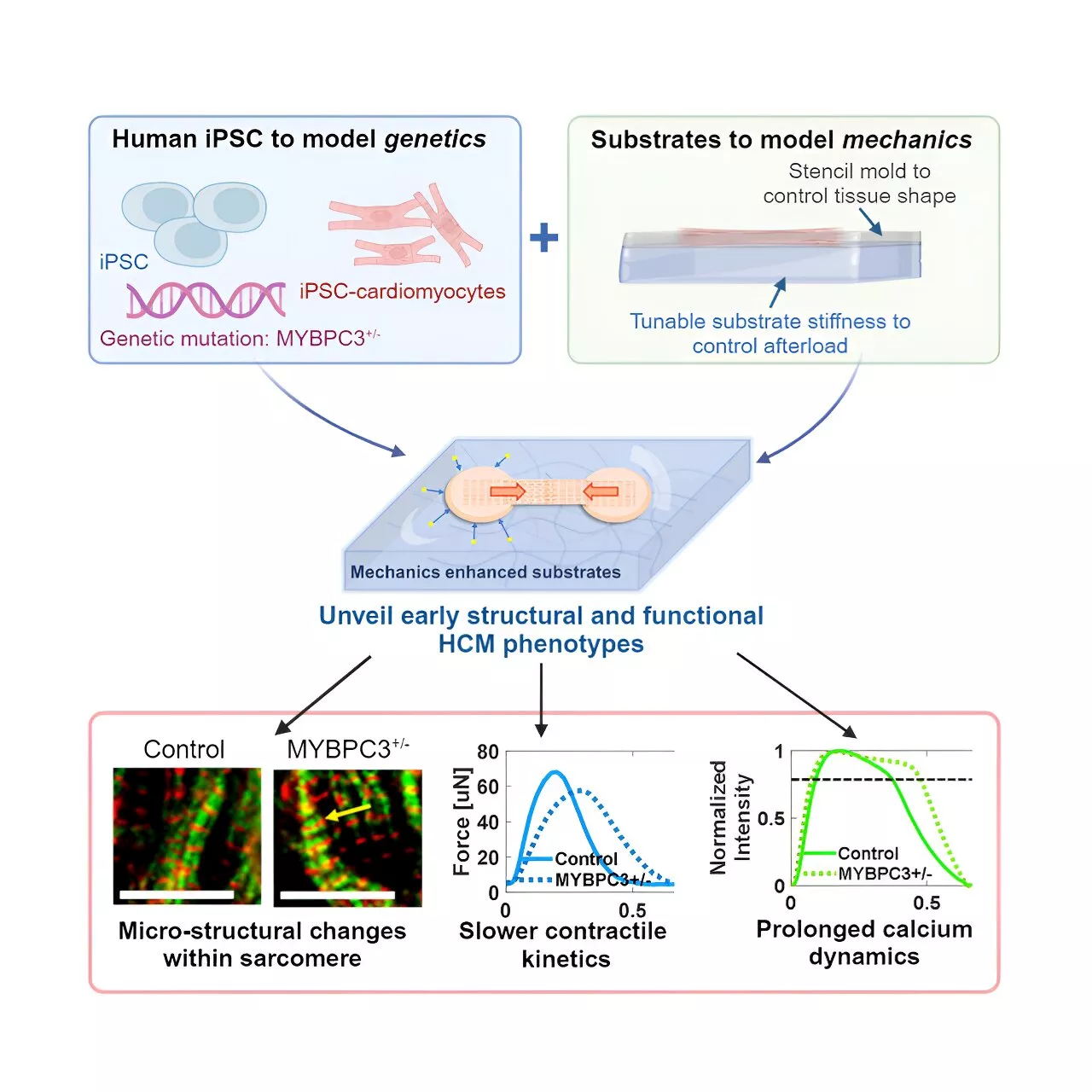
Using animals to study heart disease doesn't always translate well to human health outcomes, and human heart cells available for research don't work outside the human body.
Researchers more effectively study mutations that cause heart disease by putting cells through their paces retrieved 25 June 2024 from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-06-effectively-mutations-heart-disease-cells.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Medicine Research Health Research News Health Research Health Science Medicine Science
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers investigate the gene-brain-behavior link in autism using generative machine learningResearchers used 3D transport-based morphometry to visualize brain changes linked to 16p11.2 CNV, achieving high prediction accuracy and advancing autism precision medicine.
Researchers investigate the gene-brain-behavior link in autism using generative machine learningResearchers used 3D transport-based morphometry to visualize brain changes linked to 16p11.2 CNV, achieving high prediction accuracy and advancing autism precision medicine.
Read more »
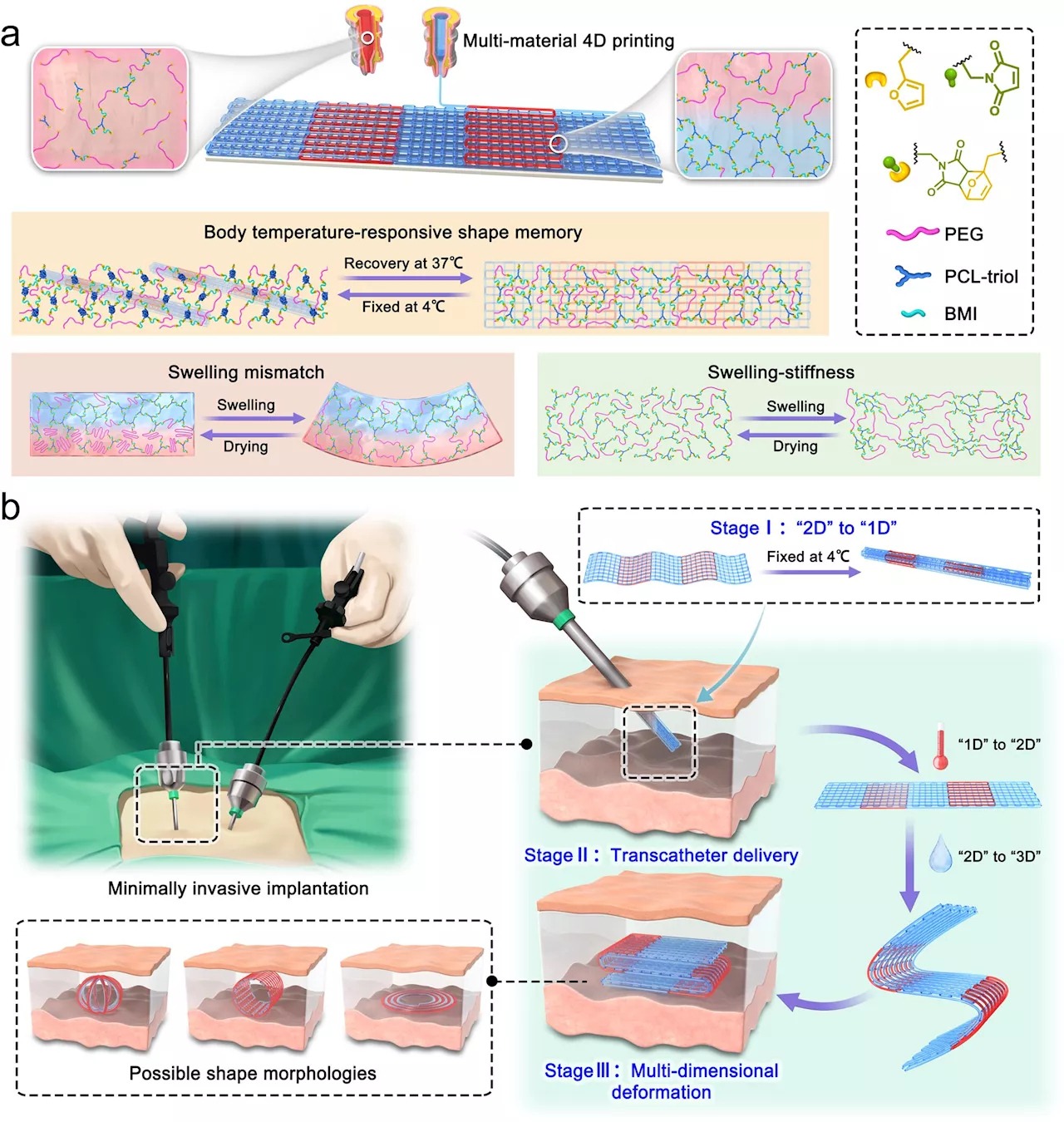 Researchers develop minimally invasive scaffold delivery system using dynamic thermoset polyurethaneRecently, researchers have developed an approach to deliver scaffolds in a minimally invasive manner through multidimensional morphing (one-dimensional to three-dimensional) by developing amphiphilic dynamic thermoset polyurethane (DTPU).
Researchers develop minimally invasive scaffold delivery system using dynamic thermoset polyurethaneRecently, researchers have developed an approach to deliver scaffolds in a minimally invasive manner through multidimensional morphing (one-dimensional to three-dimensional) by developing amphiphilic dynamic thermoset polyurethane (DTPU).
Read more »
![]() Radio trackers placed on rare beetles across DartmoorResearchers say the blue ground beetle study using 'mini backpacks' could help support conservation.
Radio trackers placed on rare beetles across DartmoorResearchers say the blue ground beetle study using 'mini backpacks' could help support conservation.
Read more »
 Crypto exchange Kraken accuses blockchain security outfit CertiK of extortionResearchers allegedly stole $3M using the vulnerability, then asked how much it was really worth
Crypto exchange Kraken accuses blockchain security outfit CertiK of extortionResearchers allegedly stole $3M using the vulnerability, then asked how much it was really worth
Read more »
 Researchers say AI accurately screens heart failure patients for clinical trial eligibilityGenerative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI) can rapidly and accurately screen patients for clinical trial eligibility, according to a new study from Mass General Brigham researchers. Such technology could make it faster and cheaper to evaluate new treatments and, ultimately, help bring successful ones to patients.
Researchers say AI accurately screens heart failure patients for clinical trial eligibilityGenerative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI) can rapidly and accurately screen patients for clinical trial eligibility, according to a new study from Mass General Brigham researchers. Such technology could make it faster and cheaper to evaluate new treatments and, ultimately, help bring successful ones to patients.
Read more »
 Researchers develop method to predict sudden cardiac death from 1-minute heart rateA new computational method developed by physicists at Tampere University can be used to estimate the risk of sudden cardiac death from a one-minute heart rate measurement at rest. The study was carried out in interdisciplinary collaboration between cardiology and computational physics.
Researchers develop method to predict sudden cardiac death from 1-minute heart rateA new computational method developed by physicists at Tampere University can be used to estimate the risk of sudden cardiac death from a one-minute heart rate measurement at rest. The study was carried out in interdisciplinary collaboration between cardiology and computational physics.
Read more »