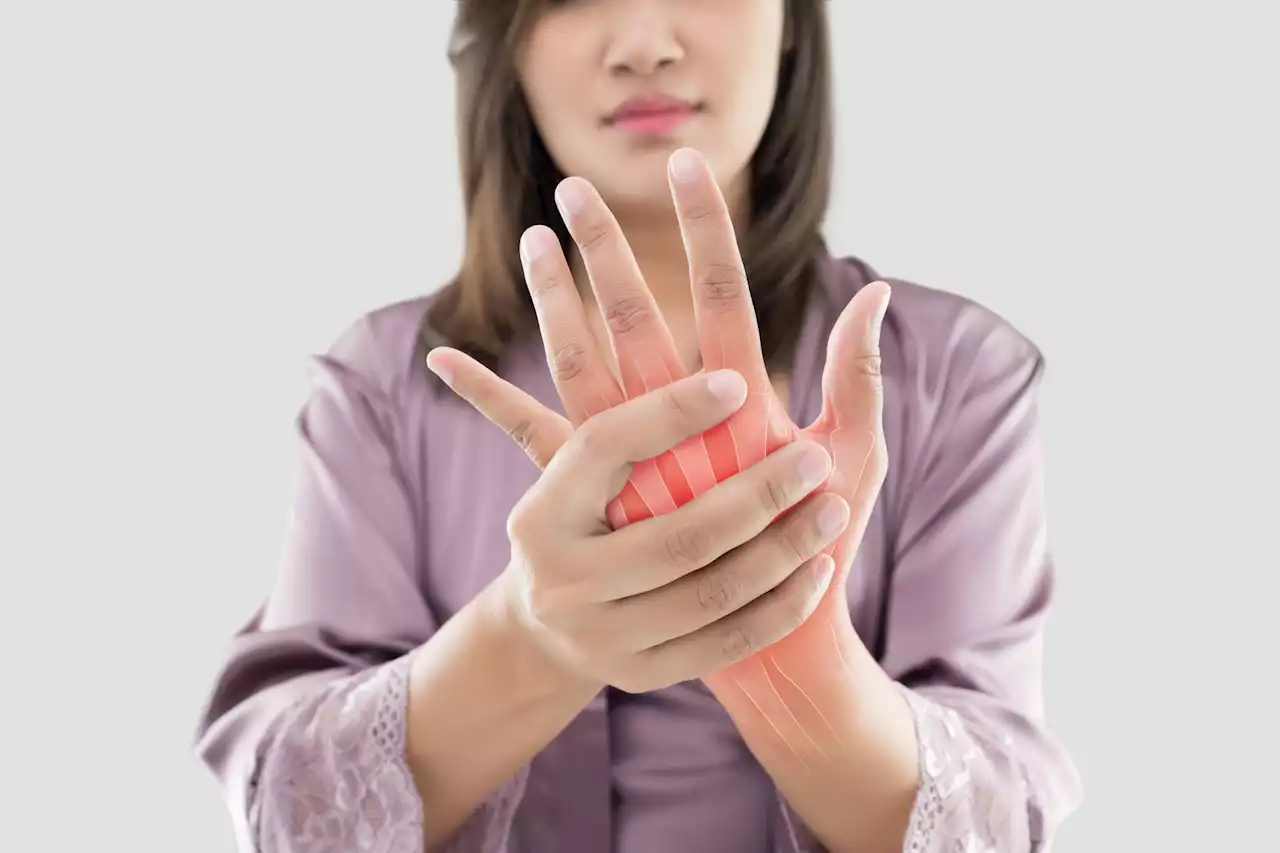
Researchers evaluated fluorescence optical imaging as a method to accurately and rapidly diagnose rheumatic diseases of the hands.
By Hugo Francisco de SouzaAug 24 2023Reviewed by Sophia Coveney In a recent study published in the journal Frontiers in Medicine, researchers evaluated fluorescence optical imaging as a method to accurately and rapidly diagnose rheumatic diseases of the hands.
Recently, fluorescence optical imaging techniques have been employed for studying these diseases. This non-invasive technique takes advantage of rheumatic inflammation-induced microcirculation impairments to identify and characterize the type of rheumatic disease. This data was compiled into three cohorts – osteoarthritis , rheumatoid arthritis , and connective tissue diseases based on clinical diagnoses. In all cohorts, diagnoses made without knowledge of FOI images were sufficient for study inclusion.
These image features included five joint-related features, two finger-related features, two nail features, four connective tissue features, and seven other features, five of which have been identified and described in this study for the first time. This resulted in the filtering and ranking features using ML models, achieved using the phi-coefficient, the relief algorithm MultiSURF, Mean Decrease Impurity , and Mean Decrease Accuracy .
Ten ML algorithms were trained and tested with cohort data, with the gradient boosting machine model identified as the best performing. The GBM model comprises a set of single ML models with stage-wise combinations of these models improving overall performance.
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers find capsules surrounding liver metastases of colorectal cancer are a healing response by the liverA study by researchers from Karolinska Institutet and physicians from Karolinska Hospital shows that a capsule of connective tissue around liver metastases from colorectal cancer improves patient survival and represents a healing response by the liver, not a phenomenon caused by the tumor itself.
Researchers find capsules surrounding liver metastases of colorectal cancer are a healing response by the liverA study by researchers from Karolinska Institutet and physicians from Karolinska Hospital shows that a capsule of connective tissue around liver metastases from colorectal cancer improves patient survival and represents a healing response by the liver, not a phenomenon caused by the tumor itself.
Read more »
 Researchers discover potential target for gastric cancers associated with Epstein-Barr virusScientists at The Wistar Institute have discovered a potential target for gastric cancers associated with Epstein-Barr Virus, and their study results are published in the journal mBio.
Researchers discover potential target for gastric cancers associated with Epstein-Barr virusScientists at The Wistar Institute have discovered a potential target for gastric cancers associated with Epstein-Barr Virus, and their study results are published in the journal mBio.
Read more »
 Researchers identify mathematical rule behind the distribution of neurons in our brainsHuman Brain Project (HBP) researchers from Forschungszentrum Jülich and the University of Cologne (Germany) have uncovered how neuron densities are distributed across and within cortical areas in the mammalian brain. They have unveiled a fundamental organizational principle of cortical cytoarchitecture: the ubiquitous lognormal distribution of neuron densities.
Researchers identify mathematical rule behind the distribution of neurons in our brainsHuman Brain Project (HBP) researchers from Forschungszentrum Jülich and the University of Cologne (Germany) have uncovered how neuron densities are distributed across and within cortical areas in the mammalian brain. They have unveiled a fundamental organizational principle of cortical cytoarchitecture: the ubiquitous lognormal distribution of neuron densities.
Read more »
 UAB researchers secure PCORI funding to compare two pathways of post-fracture patient careIn osteoporosis, bones become brittle and fragile, putting them at high risk of fractures or breaks. These 'fragility fractures' can cause pain, suffering, disability and even death, and patients have increased risks of repeat fractures.
UAB researchers secure PCORI funding to compare two pathways of post-fracture patient careIn osteoporosis, bones become brittle and fragile, putting them at high risk of fractures or breaks. These 'fragility fractures' can cause pain, suffering, disability and even death, and patients have increased risks of repeat fractures.
Read more »
 Researchers detect heart damage in kids gaming for too longAcademics said the impact of sitting for periods of six hours could be setting the stage for heart attacks and strokes
Researchers detect heart damage in kids gaming for too longAcademics said the impact of sitting for periods of six hours could be setting the stage for heart attacks and strokes
Read more »
 Water crisis should be considered as critical as climate change, researchers sayA report to mark World Water Week said the transition to circular water systems is as important as the transition to net zero.
Water crisis should be considered as critical as climate change, researchers sayA report to mark World Water Week said the transition to circular water systems is as important as the transition to net zero.
Read more »
