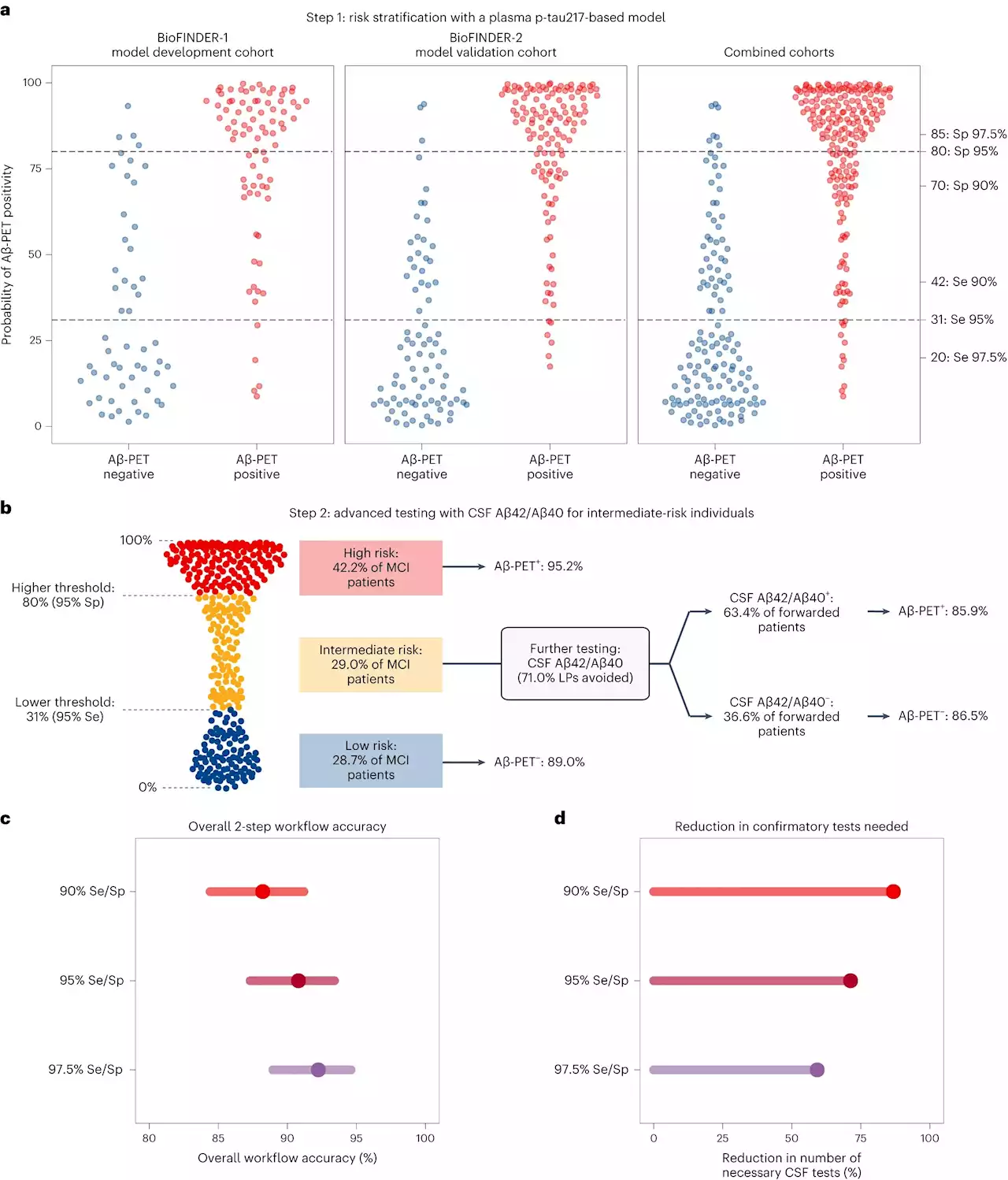
A new blood test called p-tau217 shows promise as an Alzheimer's disease biomarker, and when used in a two-step workflow very high accuracy to either identify or exclude brain amyloidosis, the most important and earliest pathology. That is an innovation now presented by researchers at the University of Gothenburg, together with colleagues at University of Lund and in Montreal, Canada.
In recent years, a lot of effort has been put on developing biomarkers in blood that could potentially help to identify Alzheimer's disease . Tau protein, in particular its phosphorylated variant —and one of the main proteins involved in AD pathology—has been the focus of extensive research and developments the last years.
However, even if promising, a concern has been that classifying early patients into either having"AD or not AD" will still result in a rather high percentage of false positives andConsidering not only ethical and psychological concerns induced by possible misdiagnosis, but also
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Discoveries on memory mechanisms could unlock new therapies for Alzheimer's and other brain diseasesScientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have made a 'paradigm shifting' discovery on the mechanisms required for learning and memory that could lead to new therapies for Alzheimer's disease and potentially Down syndrome. The study was published in the journal Nature.
Discoveries on memory mechanisms could unlock new therapies for Alzheimer's and other brain diseasesScientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have made a 'paradigm shifting' discovery on the mechanisms required for learning and memory that could lead to new therapies for Alzheimer's disease and potentially Down syndrome. The study was published in the journal Nature.
Read more »
 New study finds genetic factor fends off Alzheimer's and Parkinson'sAbout one in every five people carries a version of a gene that—although largely unsung—appears to confer protection against both Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, Stanford Medicine investigators and their colleagues have learned. These lucky people may someday benefit all the more from a vaccine that could slow or stall the progression of these two most common neurodegenerative conditions.
New study finds genetic factor fends off Alzheimer's and Parkinson'sAbout one in every five people carries a version of a gene that—although largely unsung—appears to confer protection against both Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, Stanford Medicine investigators and their colleagues have learned. These lucky people may someday benefit all the more from a vaccine that could slow or stall the progression of these two most common neurodegenerative conditions.
Read more »
 New type of road could end potholes, Surrey university research saysThermo-active roads could help stop potholes, researchers at the University of Surrey say.
New type of road could end potholes, Surrey university research saysThermo-active roads could help stop potholes, researchers at the University of Surrey say.
Read more »
 Molecule reduces inflammation in Alzheimer's modelsThough drug developers have achieved some progress in treating Alzheimer's disease with medicines that reduce amyloid-beta protein, other problems of the disease including inflammation, continue unchecked. In a new study, scientists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT describe a candidate drug that in human cell cultures and Alzheimer's mouse models reduced inflammation and improved memory.
Molecule reduces inflammation in Alzheimer's modelsThough drug developers have achieved some progress in treating Alzheimer's disease with medicines that reduce amyloid-beta protein, other problems of the disease including inflammation, continue unchecked. In a new study, scientists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT describe a candidate drug that in human cell cultures and Alzheimer's mouse models reduced inflammation and improved memory.
Read more »
 Scientists reverse Alzheimer's plaque formation in animal models by boosting activity of key ion channelLosing the activity of a key ion channel in the brain may contribute to the buildup of a devastating and toxic protein responsible for the clumps of plaque that accumulate in Alzheimer's disease, a team of neurobiologists in China has found.
Scientists reverse Alzheimer's plaque formation in animal models by boosting activity of key ion channelLosing the activity of a key ion channel in the brain may contribute to the buildup of a devastating and toxic protein responsible for the clumps of plaque that accumulate in Alzheimer's disease, a team of neurobiologists in China has found.
Read more »
 Researchers gain new insights into chromosome shortening and identify new potential cancer drug targetsA new study has provided insights into an important biological mechanism that supports survival of aggressive, hard-to-treat cancers, and in the process, has uncovered fascinating new information about how cells divide and grow.
Researchers gain new insights into chromosome shortening and identify new potential cancer drug targetsA new study has provided insights into an important biological mechanism that supports survival of aggressive, hard-to-treat cancers, and in the process, has uncovered fascinating new information about how cells divide and grow.
Read more »