Minerals found in samples of material from Antarctica could give scientists a better understanding of the surface and subsurface environment of Mars.
Minerals found in samples of material from Antarctica could give scientists a better understanding of the surface and subsurface environment of Mars, and indicate locations of potentially habitable subsurface locations., lead author Elizabeth C. Sklute, a researcher at the Planetary Science Institute, explains that in Antarctica’s Taylor Glacier brine flows out from a subsurface body of water that has been isolated for possibly thousands of years.
After scientists from the University of Tennessee collected samples of intermittent brine discharge, Sklute’s team tested them using Fourier transform infrared, Raman, visible to near-infrared, and Mössbauer spectroscopies. “We took dry samples and we analyzed them by shining light of different wavelengths at them,” Sklute said. “Each wavelength of light makes the bonds and atoms in a sample react in a different way. Using them all together, it lets us figure out what is there.”
“Combining these techniques, we have determined the detailed mineralogical assemblage of this Mars analog site and we have learned that the deposit is mostly carbonates and that the red color of Bloody Falls is from the oxidation of dissolved ferrous ions as they are exposed to air, likely in combination with other ions,” the scientist explained.
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
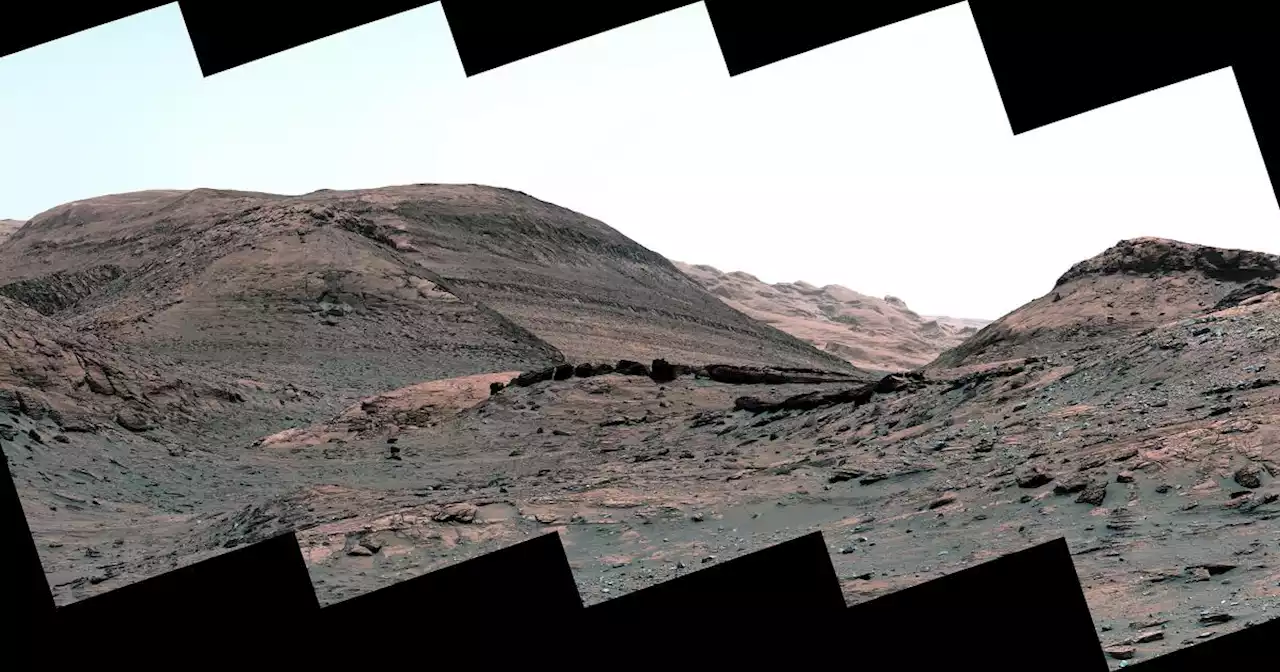 Curiosity Mars rover reveals evidence of changing climates on red planetNASA's Curiosity Mars rover found evidence of different climates on the planet occurring several billion years ago as it transitions to a mineral region.
Curiosity Mars rover reveals evidence of changing climates on red planetNASA's Curiosity Mars rover found evidence of different climates on the planet occurring several billion years ago as it transitions to a mineral region.
Read more »
 GDP update to give fresh recession clues amid soaring inflationThe final reading on first-quarter GDP out Wednesday is expected to confirm that the economy’s contraction in the spring was larger than earlier estimates.
GDP update to give fresh recession clues amid soaring inflationThe final reading on first-quarter GDP out Wednesday is expected to confirm that the economy’s contraction in the spring was larger than earlier estimates.
Read more »
Ancient wolves give clues to origins of dogsA new study helps narrow down where dogs likely came from—eastern Eurasia—while also suggesting our canine pals may have been domesticated more than once.
Read more »
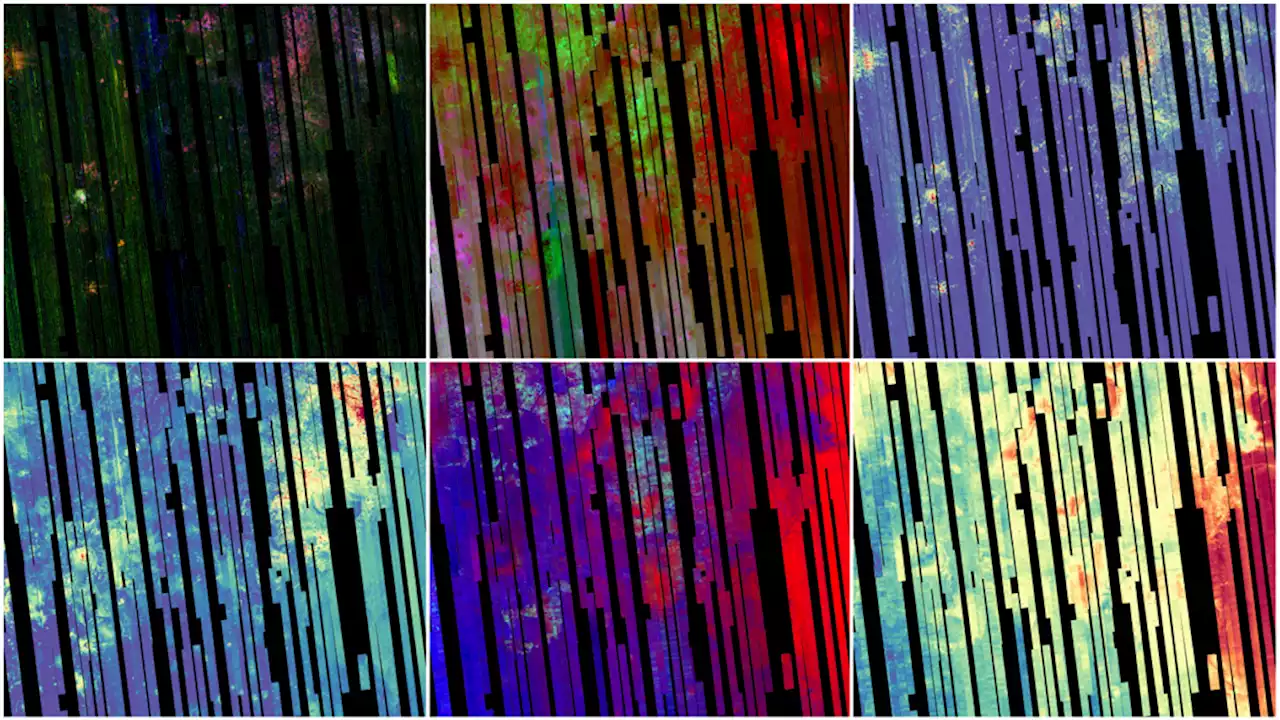 A New Map of Mars, Made From 51,000 Orbital ImagesCRISM has played a huge role in the exploration of Mars. It's about to be decommissioned, but not before giving us a gift.
A New Map of Mars, Made From 51,000 Orbital ImagesCRISM has played a huge role in the exploration of Mars. It's about to be decommissioned, but not before giving us a gift.
Read more »
 Tidal Heating Could Make Exomoons Much More Habitable (and Detectable)A new study shows how the study of tidal heating in exomoons could greatly expand the search for life in the Universe.
Tidal Heating Could Make Exomoons Much More Habitable (and Detectable)A new study shows how the study of tidal heating in exomoons could greatly expand the search for life in the Universe.
Read more »
