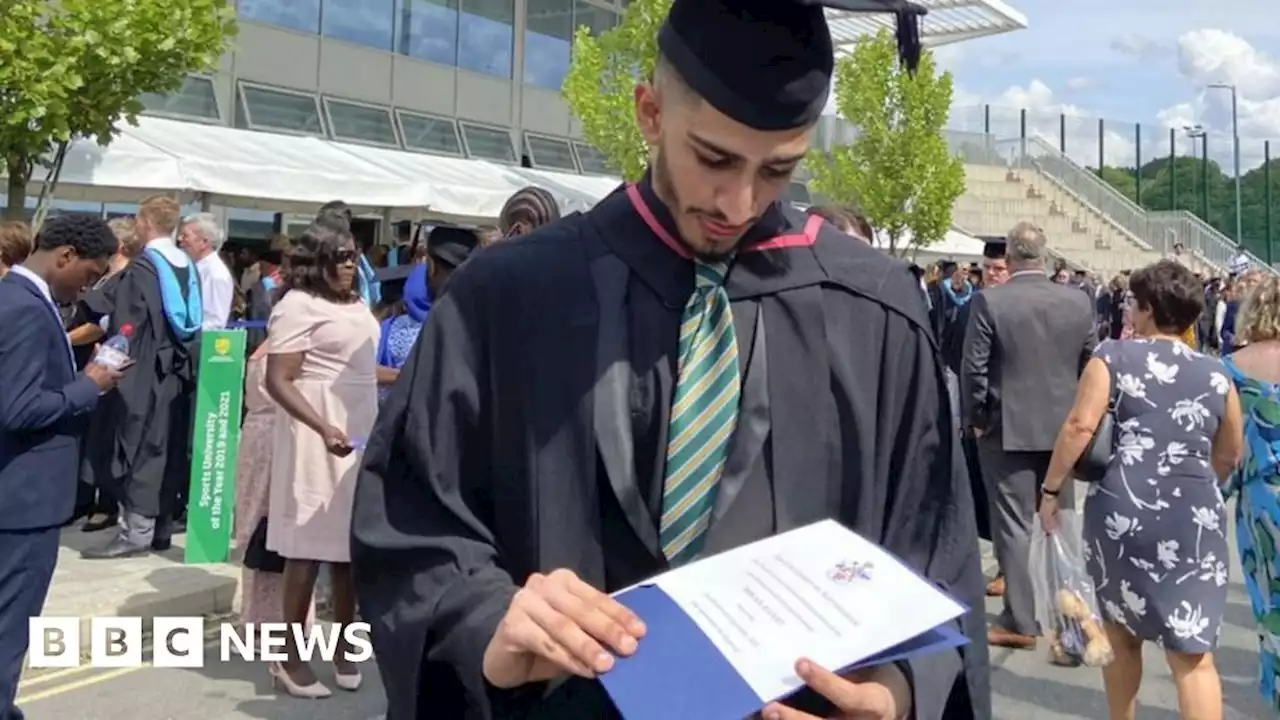
Mikail Ranjit says he did not receive the education he had paid for due to the pandemic
BBC News
Nearly 20,000 students have joined group claims through StudentGroupClaim.co.uk to take action against their universities over what they say were insufficient provisions for their education. For those unhappy with the teaching they received, the first course of action is to complain direct to the university. Only when that process is exhausted can they turn to the Office of the Independent Adjudicator.
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Effects of SARS-CoV-2-associated stress among pregnant women on development of fetus brainEffects of SARS-CoV-2-associated stress among pregnant women on development of fetus brain Brain SARSCoV2 Stress Coronavirus Disease COVID Neurology medrxivpreprint ChildrensLA PittTweet KeckMedUSC
Effects of SARS-CoV-2-associated stress among pregnant women on development of fetus brainEffects of SARS-CoV-2-associated stress among pregnant women on development of fetus brain Brain SARSCoV2 Stress Coronavirus Disease COVID Neurology medrxivpreprint ChildrensLA PittTweet KeckMedUSC
Read more »
 COVID-19 pandemic increased deaths and disease caused by tuberculosisA new report published by the World Health Organization indicated a decrease in global spending on essential TB services from US$6 billion in 2019 to US$5.4 billion in 2021.
COVID-19 pandemic increased deaths and disease caused by tuberculosisA new report published by the World Health Organization indicated a decrease in global spending on essential TB services from US$6 billion in 2019 to US$5.4 billion in 2021.
Read more »
 How COVID-19 impacted sleep and mental health among university studentsIn a recent study published in the journal PLoS ONE, researchers evaluated the effects of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) on the sleep quality and mental health (MH) of university-attending undergraduate students.
How COVID-19 impacted sleep and mental health among university studentsIn a recent study published in the journal PLoS ONE, researchers evaluated the effects of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) on the sleep quality and mental health (MH) of university-attending undergraduate students.
Read more »
 Different epidemiology of bloodstream infections in COVID-19 compared to non-COVID-19 critically ill patients: a descriptive analysis of the Eurobact II study - Critical CareBackground The study aimed to describe the epidemiology and outcomes of hospital-acquired bloodstream infections (HABSIs) between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 critically ill patients. Methods We used data from the Eurobact II study, a prospective observational multicontinental cohort study on HABSI treated in ICU. For the current analysis, we selected centers that included both COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 critically ill patients. We performed descriptive statistics between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 in terms of patients’ characteristics, source of infection and microorganism distribution. We studied the association between COVID-19 status and mortality using multivariable fragility Cox models. Results A total of 53 centers from 19 countries over the 5 continents were eligible. Overall, 829 patients (median age 65 years [IQR 55; 74]; male, n = 538 [64.9%]) were treated for a HABSI. Included patients comprised 252 (30.4%) COVID-19 and 577 (69.6%) non-COVID-19 patients. The time interval between hospital admission and HABSI was similar between both groups. Respiratory sources (40.1 vs. 26.0%, p | 0.0001) and primary HABSI (25.4% vs. 17.2%, p = 0.006) were more frequent in COVID-19 patients. COVID-19 patients had more often enterococcal (20.5% vs. 9%) and Acinetobacter spp. (18.8% vs. 13.6%) HABSIs. Bacteremic COVID-19 patients had an increased mortality hazard ratio (HR) versus non-COVID-19 patients (HR 1.91, 95% CI 1.49–2.45). Conclusions We showed that the epidemiology of HABSI differed between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients. Enterococcal HABSI predominated in COVID-19 patients. COVID-19 patients with HABSI had elevated risk of mortality. Trial registration ClinicalTrials.org number NCT03937245 . Registered 3 May 2019.
Different epidemiology of bloodstream infections in COVID-19 compared to non-COVID-19 critically ill patients: a descriptive analysis of the Eurobact II study - Critical CareBackground The study aimed to describe the epidemiology and outcomes of hospital-acquired bloodstream infections (HABSIs) between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 critically ill patients. Methods We used data from the Eurobact II study, a prospective observational multicontinental cohort study on HABSI treated in ICU. For the current analysis, we selected centers that included both COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 critically ill patients. We performed descriptive statistics between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 in terms of patients’ characteristics, source of infection and microorganism distribution. We studied the association between COVID-19 status and mortality using multivariable fragility Cox models. Results A total of 53 centers from 19 countries over the 5 continents were eligible. Overall, 829 patients (median age 65 years [IQR 55; 74]; male, n = 538 [64.9%]) were treated for a HABSI. Included patients comprised 252 (30.4%) COVID-19 and 577 (69.6%) non-COVID-19 patients. The time interval between hospital admission and HABSI was similar between both groups. Respiratory sources (40.1 vs. 26.0%, p | 0.0001) and primary HABSI (25.4% vs. 17.2%, p = 0.006) were more frequent in COVID-19 patients. COVID-19 patients had more often enterococcal (20.5% vs. 9%) and Acinetobacter spp. (18.8% vs. 13.6%) HABSIs. Bacteremic COVID-19 patients had an increased mortality hazard ratio (HR) versus non-COVID-19 patients (HR 1.91, 95% CI 1.49–2.45). Conclusions We showed that the epidemiology of HABSI differed between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients. Enterococcal HABSI predominated in COVID-19 patients. COVID-19 patients with HABSI had elevated risk of mortality. Trial registration ClinicalTrials.org number NCT03937245 . Registered 3 May 2019.
Read more »
