Alex Albon is recovering after suffering respiratory failure following appendicitis surgery, with the Williams F1 driver having spent time in intensive care Full story ⬇️
Albon fell ill on Saturday morning and had to sit out the rest of the Italian Grand Prix weekend, with hisOn Monday Williams announced that Albon suffered"complications which led to respiratory failure" after the procedure, which meant Albon had to be re-intubated and moved to the San Gerardo hospital's intensive care unit.
"Following surgery, Alex suffered with unexpected post-operative anaesthetic complications which led to respiratory failure, a known but uncommon complication. He was re-intubated and transferred to intensive care for support. The team added that Albon is still hoping to be able to return at the Singapore Grand Prix on last weekend of September.
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Strategies for lung- and diaphragm-protective ventilation in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: a physiological trial - Critical CareBackground Insufficient or excessive respiratory effort during acute hypoxemic respiratory failure (AHRF) increases the risk of lung and diaphragm injury. We sought to establish whether respiratory effort can be optimized to achieve lung- and diaphragm-protective (LDP) targets (esophageal pressure swing − 3 to − 8 cm H2O; dynamic transpulmonary driving pressure ≤ 15 cm H2O) during AHRF. Methods In patients with early AHRF, spontaneous breathing was initiated as soon as passive ventilation was not deemed mandatory. Inspiratory pressure, sedation, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), and sweep gas flow (in patients receiving veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO)) were systematically titrated to achieve LDP targets. Additionally, partial neuromuscular blockade (pNMBA) was administered in patients with refractory excessive respiratory effort. Results Of 30 patients enrolled, most had severe AHRF; 16 required VV-ECMO. Respiratory effort was absent in all at enrolment. After initiating spontaneous breathing, most exhibited high respiratory effort and only 6/30 met LDP targets. After titrating ventilation, sedation, and sweep gas flow, LDP targets were achieved in 20/30. LDP targets were more likely to be achieved in patients on VV-ECMO (median OR 10, 95% CrI 2, 81) and at the PEEP level associated with improved dynamic compliance (median OR 33, 95% CrI 5, 898). Administration of pNMBA to patients with refractory excessive effort was well-tolerated and effectively achieved LDP targets. Conclusion Respiratory effort is frequently absent under deep sedation but becomes excessive when spontaneous breathing is permitted in patients with moderate or severe AHRF. Systematically titrating ventilation and sedation can optimize respiratory effort for lung and diaphragm protection in most patients. VV-ECMO can greatly facilitate the delivery of a LDP strategy. Trial registration: This trial was registered in Clinicaltrials.gov in August 2018 (NCT03612583).
Strategies for lung- and diaphragm-protective ventilation in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: a physiological trial - Critical CareBackground Insufficient or excessive respiratory effort during acute hypoxemic respiratory failure (AHRF) increases the risk of lung and diaphragm injury. We sought to establish whether respiratory effort can be optimized to achieve lung- and diaphragm-protective (LDP) targets (esophageal pressure swing − 3 to − 8 cm H2O; dynamic transpulmonary driving pressure ≤ 15 cm H2O) during AHRF. Methods In patients with early AHRF, spontaneous breathing was initiated as soon as passive ventilation was not deemed mandatory. Inspiratory pressure, sedation, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), and sweep gas flow (in patients receiving veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO)) were systematically titrated to achieve LDP targets. Additionally, partial neuromuscular blockade (pNMBA) was administered in patients with refractory excessive respiratory effort. Results Of 30 patients enrolled, most had severe AHRF; 16 required VV-ECMO. Respiratory effort was absent in all at enrolment. After initiating spontaneous breathing, most exhibited high respiratory effort and only 6/30 met LDP targets. After titrating ventilation, sedation, and sweep gas flow, LDP targets were achieved in 20/30. LDP targets were more likely to be achieved in patients on VV-ECMO (median OR 10, 95% CrI 2, 81) and at the PEEP level associated with improved dynamic compliance (median OR 33, 95% CrI 5, 898). Administration of pNMBA to patients with refractory excessive effort was well-tolerated and effectively achieved LDP targets. Conclusion Respiratory effort is frequently absent under deep sedation but becomes excessive when spontaneous breathing is permitted in patients with moderate or severe AHRF. Systematically titrating ventilation and sedation can optimize respiratory effort for lung and diaphragm protection in most patients. VV-ECMO can greatly facilitate the delivery of a LDP strategy. Trial registration: This trial was registered in Clinicaltrials.gov in August 2018 (NCT03612583).
Read more »
 Nyck de Vries says he was 'chilling in Paddock Club' before shock Williams call-upNyck de Vries went from enjoying a cappuccino in the Paddock Club to replacing Alex Albon at Williams in the blink of an eye at Monza.
Nyck de Vries says he was 'chilling in Paddock Club' before shock Williams call-upNyck de Vries went from enjoying a cappuccino in the Paddock Club to replacing Alex Albon at Williams in the blink of an eye at Monza.
Read more »
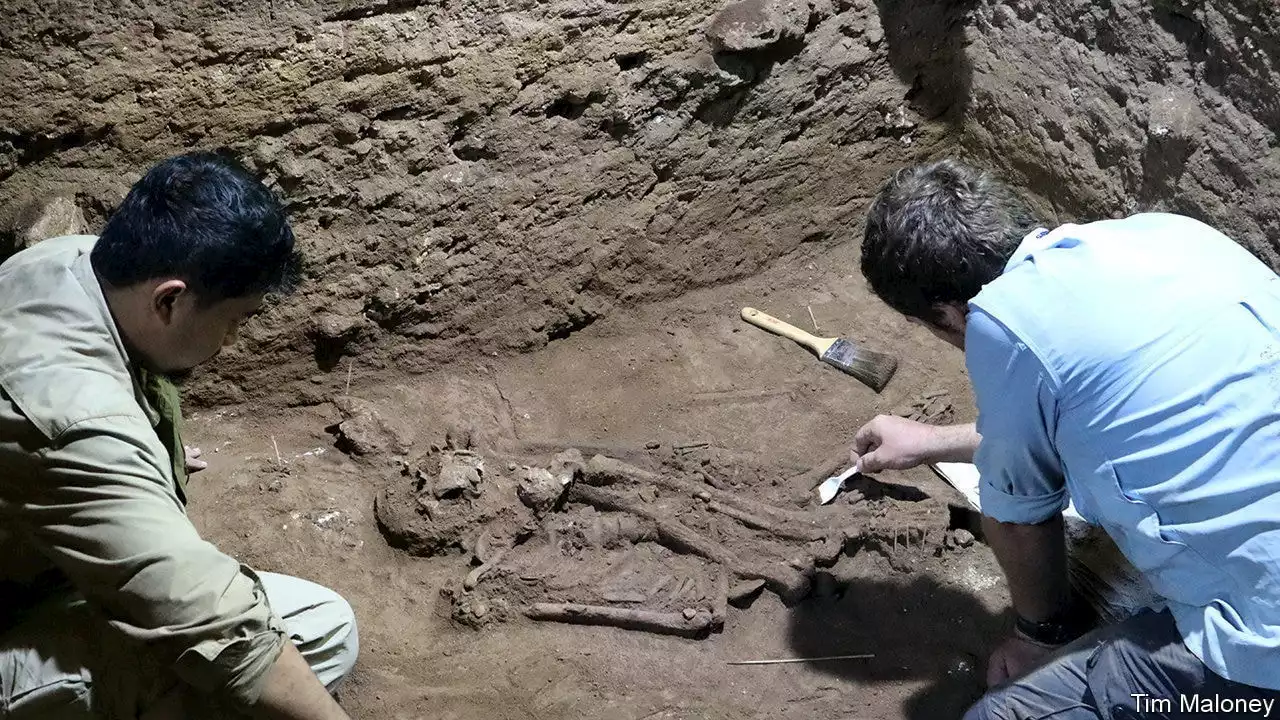 Humans were performing amputations earlier than thoughtScientists have excavated the oldest grave ever found in South-East Asia. The 31,000-year-old skeleton they found was missing its left foot and part of the left leg, showing compelling signs of surgical amputation
Humans were performing amputations earlier than thoughtScientists have excavated the oldest grave ever found in South-East Asia. The 31,000-year-old skeleton they found was missing its left foot and part of the left leg, showing compelling signs of surgical amputation
Read more »
 Discovery of antibodies that may eliminate the need for COVID vaccinesIn a recent study published in the journal Communications Biology , researchers evaluated the efficacy of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)...
Discovery of antibodies that may eliminate the need for COVID vaccinesIn a recent study published in the journal Communications Biology , researchers evaluated the efficacy of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)...
Read more »
 Small molecule inhibitor found to be effective against SARS-CoV-2 variantsIn a new study, researchers developed RK-33, a small molecule inhibitor of DDX3, and evaluated its efficacy against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants of concern (VOCs).
Small molecule inhibitor found to be effective against SARS-CoV-2 variantsIn a new study, researchers developed RK-33, a small molecule inhibitor of DDX3, and evaluated its efficacy against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants of concern (VOCs).
Read more »
