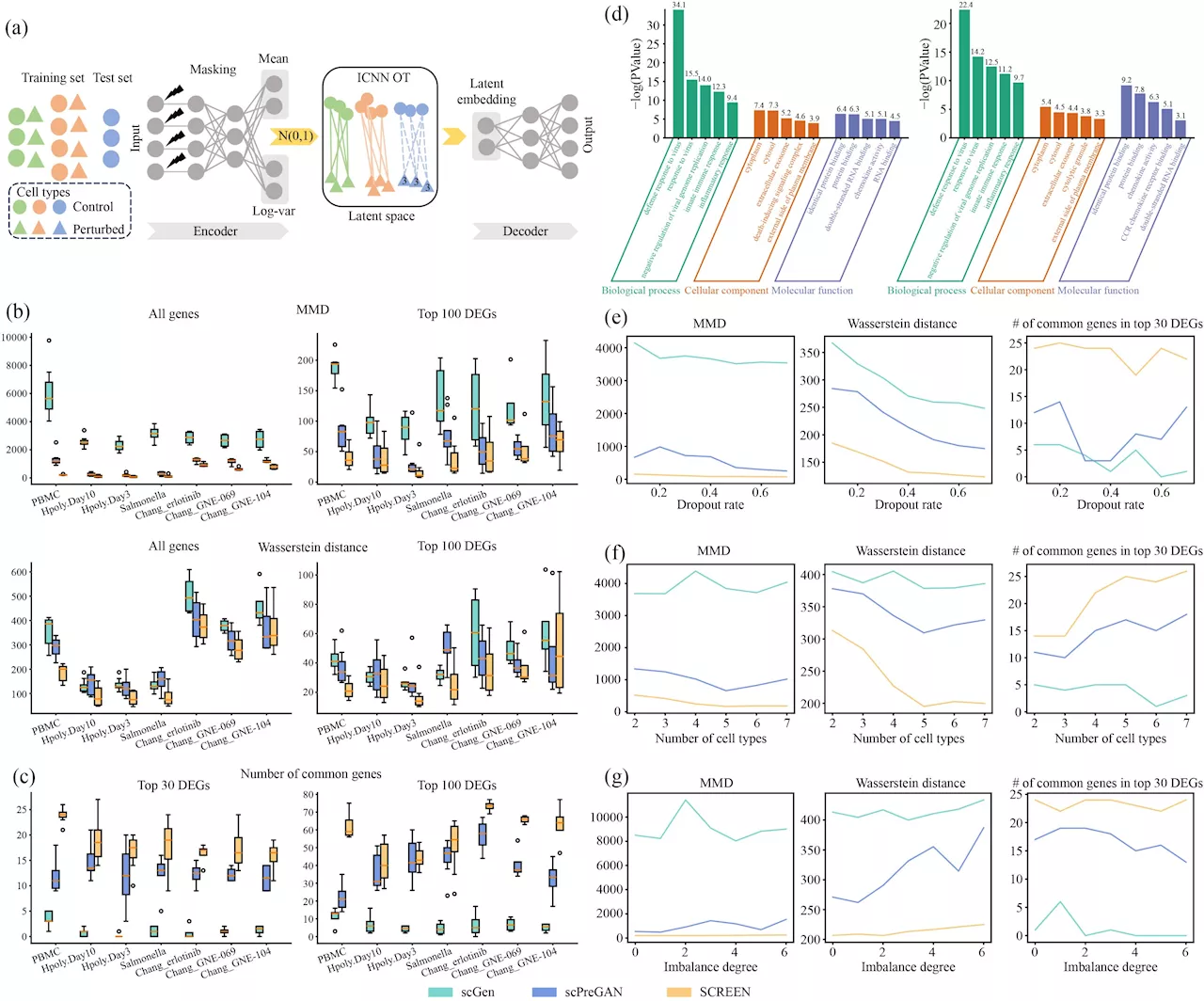
The rapid development of single-cell RNA sequencing technologies has made it possible to study the impact of external perturbations on gene expression at the level of individual cells.
A novel approach for predicting single-cell gene expression perturbation responses retrieved 8 July 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-07-approach-cell-gene-perturbation-responses.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.3 hours agoUse this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Physics News Science News Technology News Physics Materials Nanotech Technology Science
South Africa Latest News, South Africa Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Spliceosomes: New technique tracks proteins involved in RNA splicingBodybuilders and cellular mechanisms agree generating protein is a heavy lift. To complete the task, cells rely on complexes called spliceosomes. These molecular machines snip extra bits out of our genes' RNA copies and piece together precise instructions for protein-building.
Spliceosomes: New technique tracks proteins involved in RNA splicingBodybuilders and cellular mechanisms agree generating protein is a heavy lift. To complete the task, cells rely on complexes called spliceosomes. These molecular machines snip extra bits out of our genes' RNA copies and piece together precise instructions for protein-building.
Read more »
 How human derived RNA fragments help the Hepatitis E virusWhy does Hepatitis E become chronic in some patients, and why do medications not work? To find out, an international research team led by scientists from Bochum observed a patient with chronic Hepatitis E infection over a year.
How human derived RNA fragments help the Hepatitis E virusWhy does Hepatitis E become chronic in some patients, and why do medications not work? To find out, an international research team led by scientists from Bochum observed a patient with chronic Hepatitis E infection over a year.
Read more »
 Revolutionary Genetics Research Shows RNA May Rule Our GenomeScientists have recently discovered thousands of active RNA molecules that can control the human body
Revolutionary Genetics Research Shows RNA May Rule Our GenomeScientists have recently discovered thousands of active RNA molecules that can control the human body
Read more »
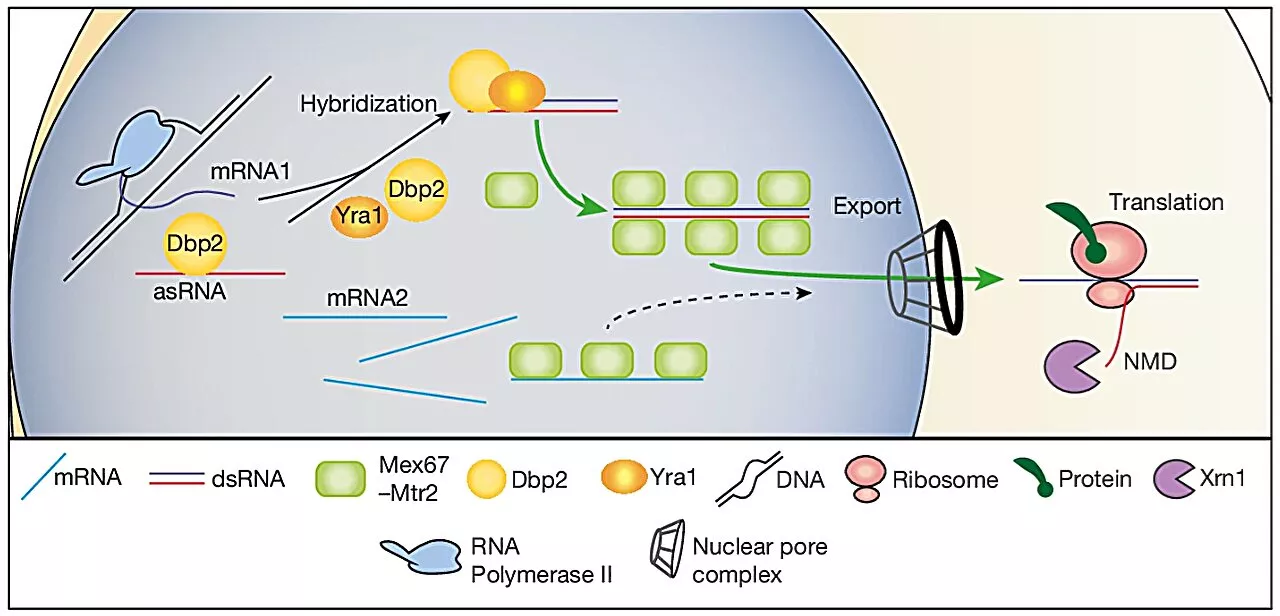 Non-coding RNA acts as 'superhighway' for gene expression, study findsThe function of non-coding RNA in the cell has long been a mystery to researchers. Unlike coding RNA, non-coding RNA does not produce proteins—yet it exists in large quantities.
Non-coding RNA acts as 'superhighway' for gene expression, study findsThe function of non-coding RNA in the cell has long been a mystery to researchers. Unlike coding RNA, non-coding RNA does not produce proteins—yet it exists in large quantities.
Read more »
 Researchers develop RNA-targeting technology for precisely manipulating parts of human genesResearchers at the University of Toronto have harnessed a bacterial immune defense system, known as CRISPR, to efficiently and precisely control the process of RNA splicing.
Researchers develop RNA-targeting technology for precisely manipulating parts of human genesResearchers at the University of Toronto have harnessed a bacterial immune defense system, known as CRISPR, to efficiently and precisely control the process of RNA splicing.
Read more »
 Researchers develop RNA-targeting technology for precisely manipulating parts of human genesResearchers have harnessed a bacterial immune defense system, known as CRISPR, to efficiently and precisely control the process of RNA splicing. The technology opens the door to new applications, including systematically interrogating the functions of parts of genes and correcting splicing deficiencies that underlie numerous diseases and disorders.
Researchers develop RNA-targeting technology for precisely manipulating parts of human genesResearchers have harnessed a bacterial immune defense system, known as CRISPR, to efficiently and precisely control the process of RNA splicing. The technology opens the door to new applications, including systematically interrogating the functions of parts of genes and correcting splicing deficiencies that underlie numerous diseases and disorders.
Read more »